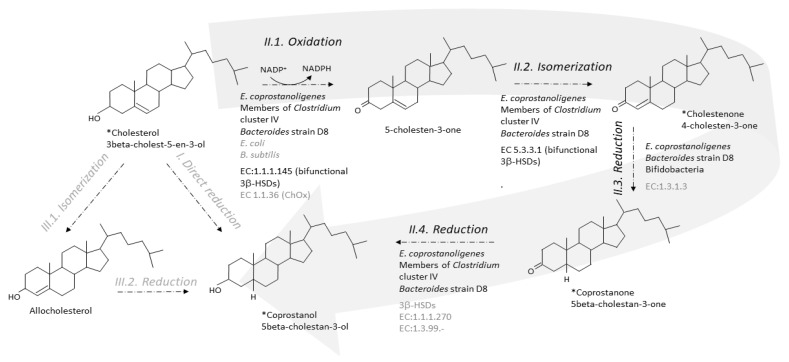
Figure 3.
Direct and indirect pathways for the conversion of cholesterol to coprostanol by the gut microbiota. The indirect pathway (II, large grey arrow) is by far the most probable as evidenced by identification of the intermediates in crude feces and cultures of pure active strains. The direct pathway (I) cannot be excluded but never received any proof of evidence. Note that isomerization of cholesterol to allocholesterol and then reduction of allocholesterol to coprostanol (pathway III) are chemical reactions that, until proved otherwise, do not proceed in any organism. * Intermediate seen in GC-MS analyses of feces or pure active cultures. Micro-organisms and enzymes involved in the considered reaction are mentioned; black and grey characters correspond to confirmed and uncertain knowledge, respectively. A micro-organism is confirmed if it has been shown to process to the reaction in pure culture. An enzyme is confirmed if it has been purified and characterized in at least one gut micro-organism.