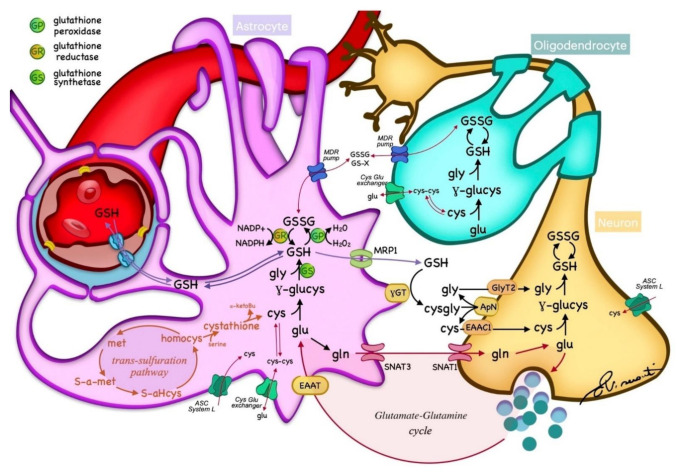
Figure 1.
Glutathione (GSH) metabolism within the nervous tissue. GSH is synthesized in the cytoplasm of neurons and glia from essential amino acids, and catabolized through hydrolysis in the cell membranes. GSH acts as a reducing agent by donating an electron to H2O2, leading to the formation of H2O, O2, and glutathione disulfide (GSSG), which is regenerated by glutathione reductase (GR) from NADPH. The transportation of GSH and essential metabolites is regulated by different transporters across cell membranes. Cys—cysteine; glu—glutamate; gln—glycine; met—methionine; homocys—homocysteine; MPR—multidrug resistance pump; γGT—γ-glutamyltransferase; γ-glucys—γ-glutamylcysteine; EAAT—excitatory amino acid transporter; SNAT—sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporter; ASC—alanine, serine, and cysteine transport system.