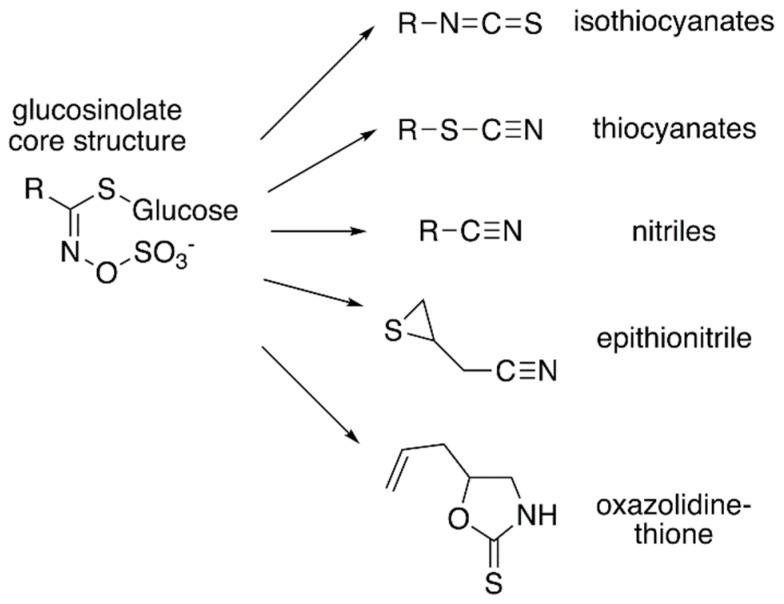
Figure 1.
Core glucosinolate structure and hydrolysis product diversity. The core chemical structure of glucosinolates (left) consists of a β–D–glucosyl residue linked via a sulfur to a (Z)–N–hydroximinosulfate ester with and a variable amino acid-derived R group. Modifications of the aliphatic, aromatic, or indole R-group leads to the chemical diversity of this class of specialized metabolites. Hydrolysis of various glucosinolates leads to an array of bioactive molecules (right), including isothiocyanates, thiocyanates, nitriles, epithionitrile, and oxazolidine-thione.