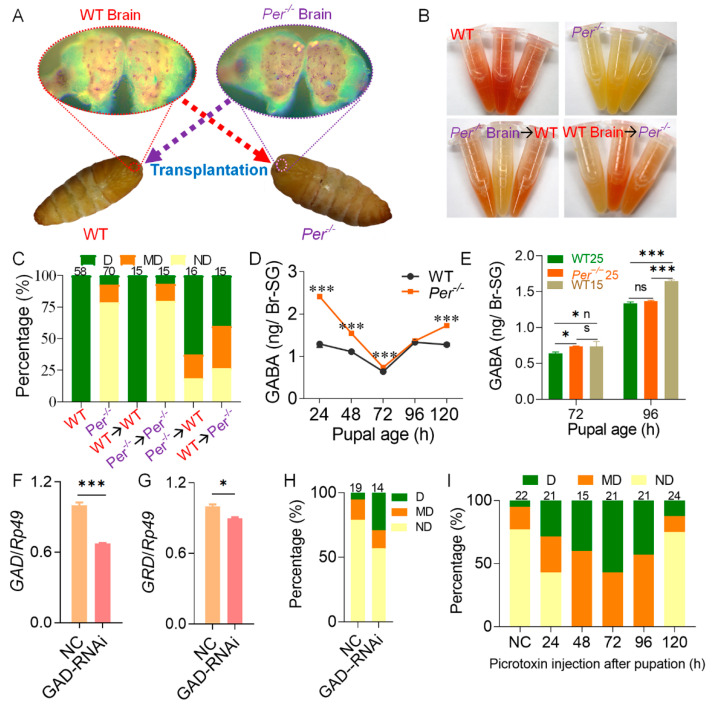
Figure 4.
Deletion of Per affects diapause via the neurotransmitter GABA in the pupal brain. (A) Schematic of brain transplantation. Brain transplantation was performed on female pupae with ages of 10 h (±1 h). (B) Effect of brain transplantation on the content of 3-hydroxykynurenine. The 3-hydroxykynurenine content of intact ovaries from moth ages of 3–6 h was detected using Ehrlich’s diazo reaction. (C) Effect of brain transplantation on egg diapause. Absorbance of Ehrlich’s diazo reaction was used to judge the diapause types according to the diapause classification criteria (n = 15–70 female moths). (D,E) The content of GABA in Br-SG of pupae. The parental embryonic incubation was 25LD (D), 25LD and 15LD (E). (F,G) Efficiency of interference with GAD on the diapause of Per−/−. GAD-RNAi, GAD interference dsRNA was injected at pupal age of 48 h. NC, invalid interference fragments were injected. The mRNA levels of GAD (F) and GRD (G) in Br-SG were measured 24 h after injection (n = 3). (H) Effect of GAD-RNAi on diapause. The ND batches rate was 79% in NC and the ND rate declined to 57% after GAD-RNAi (n = 14–19 batches). (I) Picrotoxin treatment can rescue the diapause of Per−/−. 90 μg picrotoxin was injected into each Per−/− pupa. The control (NC) was injected with 30 μL sterile water at pupal age of 24 h. The diapause was determined by the content of 3-hydroxykynurenine in the moth ovaries ages of 3–6 h (n = 15–24 female moths). In figure (D–G), * p < 0.05; *** p < 0.001, n = 3. In figures (F–I), eggs were incubated in 25LD.