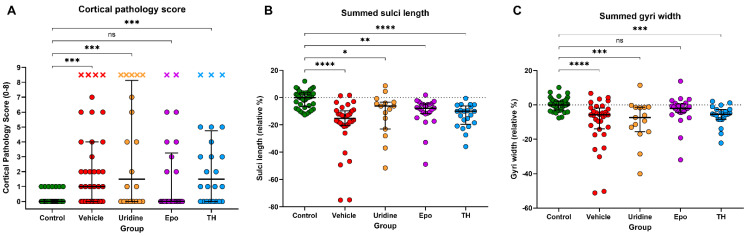
Figure 3.
Cortical Pathology and Morphology. The median and IQR is plotted on each graph. (A) Surviving animals received combined scores of 0–8 (0–4 cortical pathology + 0–4 mineralization) while animals that died after the HIH insult received a score of 8.5. Control animals had a median cortical pathology score of 0 with no deaths. Median scores significantly increased in the Veh group to 1 and in the Ur and TH groups to 1.5. Deaths also increased in the Veh, Ur, and TH groups to 4, 5, and 3, respectively. Compared to controls, number of deaths in the Epo group increased to 2. (B) Summed sulci length in the HIH groups relative to the control group. After calculating the sum of the lengths of each sulci, the HIH groups all displayed a shorter sum of sulcal length than the control group. On average, HIH brains sulci were 8.8% (3.3–16.9%) shorter than control brains. (C) Summed gyri widths in the HIH–exposed groups relative to control median. Similar to the summing of sulci, the summing of the width of each gyri showed that control brains had significantly wider gyri than Veh (3.6%; 0.1–9.5%), Ur (7.3%; 1.4–15.6%) and TH (5.4%; 2.6–8.4%) brains. Epo brains exhibited summed gyral widths more similar to control brains. * Denotes p–value < 0.05, ** denotes p–value < 0.01, *** denotes p–value < 0.001, **** denotes p–value < 0.0001, and ns denotes no significant difference.