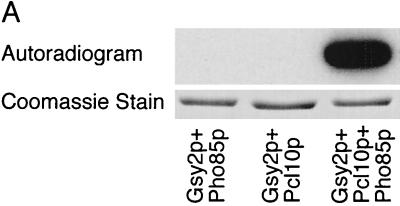
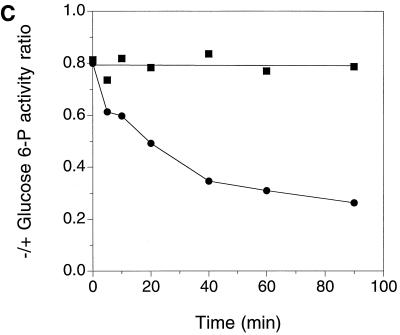
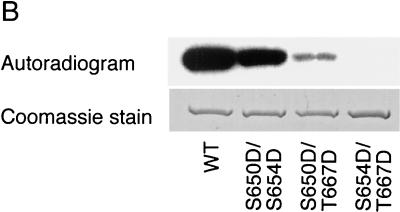
FIG. 1.
Expression of a functional Pho85p-Pcl10p complex in E. coli. (A) Phosphorylation of Gsy2p by lysates of E. coli coexpressing Pho85p and Pcl10p. Cell lysates were prepared from E. coli carrying either pET-HisPHO85, pACYC-HAPCL10, or both. Purified, recombinant Gsy2p was incubated with these extracts in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP and MgCl2. The Gsy2p was then repurified from the incubation mixture with Ni2+-NTA–agarose and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. (B) Phosphorylation of mutant Gsy2p. Lysates from E. coli expressing both Pho85p and Pcl10p were used to phosphorylate either wild-type (WT) Gsy2p or Gsy2p where combinations of the known phosphorylation sites (Ser650, Ser654, and Thr667) were mutated to aspartic acid. The phosphorylated Gsy2p was recovered and analyzed as described above. (C) Phosphorylation and inactivation of Gsy2p. Purified recombinant Gsy2p was incubated with lysates prepared from E. coli coexpressing Pho85p and Pcl10p either in the presence of MgCl2 and ATP (●) or MgCl2 alone (■). At the indicated times, aliquots were removed and the −/+ glucose-6-P activity of glycogen was determined.