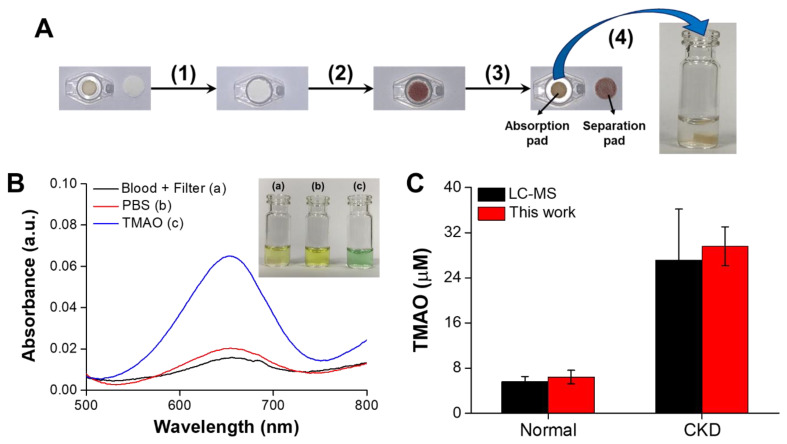
Figure 5.
(A) The design and principle of colourimetric TMAO detection using whole blood based on the combination of a plasma separation pad as a erythrocyte trap and an absorption pad as serum/plasma trap to filter erythrocytes and haemachrome as follows: (1) the absorption pad is covered with the separation pad; (2) 50 μL of whole blood is dropped on the separation pad; (3) the serum/plasma is collected in the absorption pad and (4) the absorption pad with serum/plasma is placed into a glass vial for TMAO detection; (B) UV-vis absorption spectra and visual colour changes of the catalysed oxidation of TMB in two groups to confirm that the erythrocytes and haemachrome of whole blood could be filtered and that normal serum/plasma would not cause proton depletion, similar to PBS; the inset is a corresponding digital photo; (C) TMAO concentrations in 8 whole blood samples from normal rats and 8 whole blood samples from CKD that were measured using LC–MS and the proposed colourimetric assay for CKD monitoring. The values are means ± SD (n = 8).