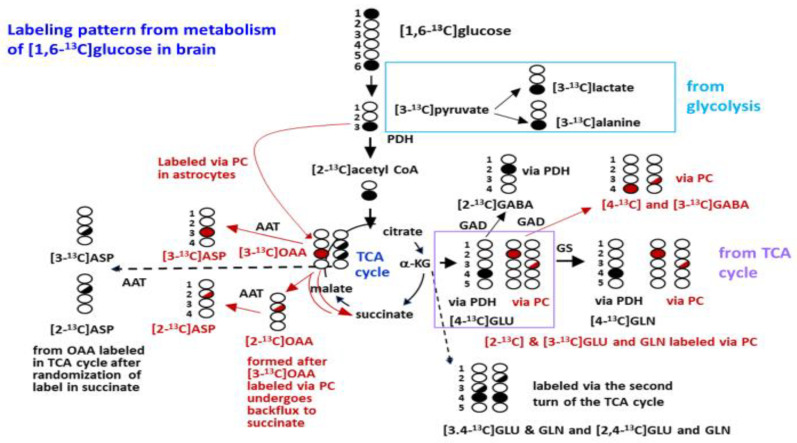
Figure 1.
Labeling pattern from the metabolism of [1,6-13C]glucose in the brain. The labeling pattern from the metabolism of [1,6-13C]glucose via glycolysis, pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) and metabolism in the first turn of the TCA cycle and subsequent formation of glutamate is shown in black circles. Formation of glutamate C4 (GLU C4) from metabolism in the first turn of the TCA cycle, which is stronger in neurons but also occurs in astrocytes, and subsequent conversion to glutamine C4 (GLN C4) in astrocytes is indicated by black circles. Further metabolism of α-ketoglutarate C4 (α-KG) in the TCA cycle results in randomization of the label in the symmetrical molecule succinate and leads to formation of malate and oxaloacetate (OAA) equally labeled in the C2 and C3 positions (half-filled black circles). OAA can remain in the TCA cycle or be transaminated to form aspartate (ASP C2 and C3). Labeling of OAA from metabolism via the pyruvate carboxylase (PC) pathway in astrocytes leading is shown in red circles. Backflux of OAA C3 labeled via PC leads to partial labeling of OAA C2 (partially filled red circle). Metabolism of OAA labeled via PC leads to labeling of GLU and GLN in the C2 indicated by red circles. Some labeling in the C3 positions of GLU and GLN occurs from the backflux labeling in OAA. GABA C2 is formed from glutamate labeled via PDH in the first turn of the TCA cycle (black circles) and GABA C4 and some GABA C3 is labeled from precursors formed via PC (red circles). For simplicity, labeling from the first turn of the TCA cycle is shown and labeling of GLU and GLN from the second turn is shown. It should be noted that GLU C3 and C2 are also labeled in the second turn of the TCA cycle and GABA C3 can be formed from GLU C3 formed in neurons. Additional details of the labeling and pathways are given in the Section 2. Abbreviations: AAT, aspartate aminotransferase; GABA, Υ-aminobutyric acid; GAD, glutamic acid decarboxylase; GLU, glutamate; GLN, glutamine; GS, glutamine synthetase; OAA, oxaloacetate; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase complex; PC, pyruvate carboxylase. (Figure reproduced with permission from Ferreira et al. [30]).