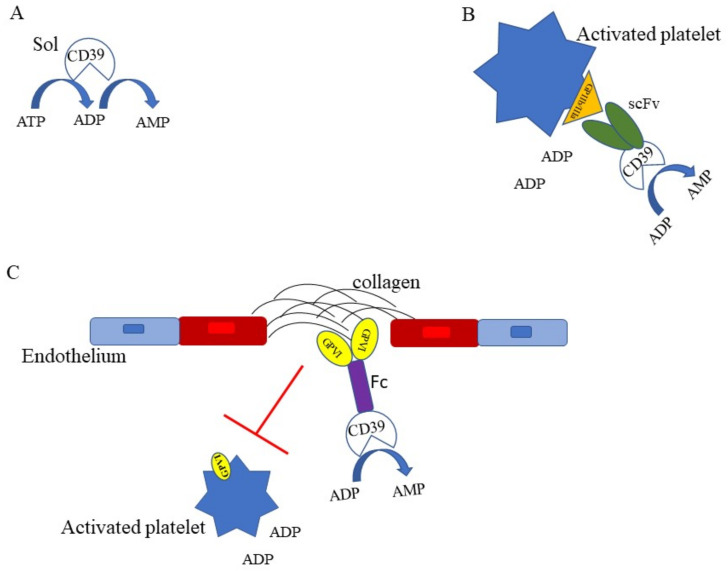
Figure 2.
Targeting NTPDase1/CD39 in thrombosis. (A) Recombinant soluble CD39 (solCD39) [39,53,94] through its ATPase and ADPase activities inhibits ADP-mediated platelet activation and aggregation. (B) CD39, fused with a single-chain antibody (scFv) specific for GPIIb/IIIa [94,95,96], expressed on activated platelets, contributes to reduce ADP concentration, providing strong anti-thrombotic effects. (C) The glycoprotein VI (GPVI)Fc-fusion protein is combined to soluble CD39 [97]. The GPVI-Fc inhibits the interaction of GPVI expressed on platelets with vascular collagen in plaques while CD39 reduces the concentrations of ATP/ADP, resulting in a strong inhibition of platelets adhesion and aggregation.