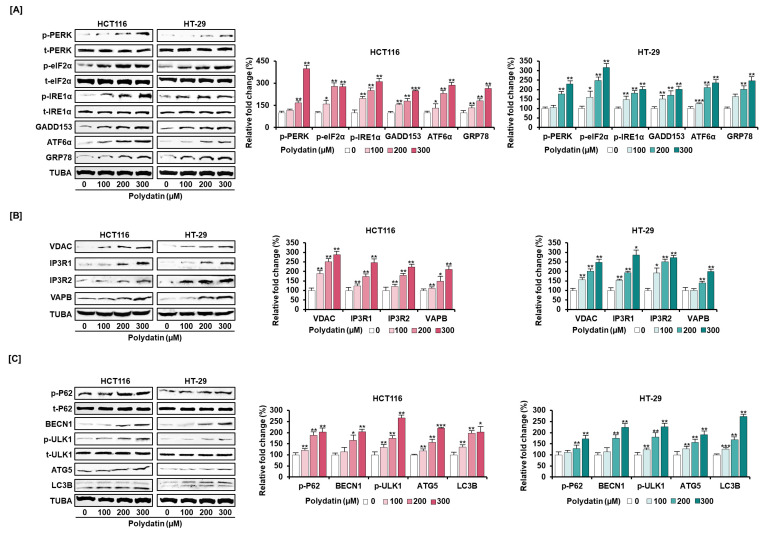
Figure 5.
Dose-dependent stimulatory effects of polydatin on protein levels related to anticancer ability. (A) The protein expression of ER stress inducers—PKR-like ER-resident kinase (p-PERK), inositol-requiring enzyme 1α (IRE1α), and activating transcription factor 6α (ATF6α), ER stress sensor—eukaryotic translation-initiation factor 2α (p-eIF2α), and growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible gene 153 (GADD153), and the upregulation protein of ER stress sensor—glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78), when HCT116 and HT-29 cells were treated with diverse concentrations of polydatin. (B) Effects of polydatin on ER-mitochondria-tethering proteins (VDAC, IP3R1, IP3R2, and VAPB) in HCT116 and HT-29 cells by Western blotting. (C) The protein levels of phosphorylated P62 (p-P62), beclin-1 (BECN1), phosphorylated UNC-51-like kinase 1 (p-ULK1), autophagy-related 5 (ATG5), and microtubule-associated proteins 1A/1B light chain 3B (LC3B) implicated in autophagy. The expression of each protein was normalized compared with TUBA or each total protein. The asterisks mean statistical variation between polydatin-treated and DMSO-treated groups (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001).