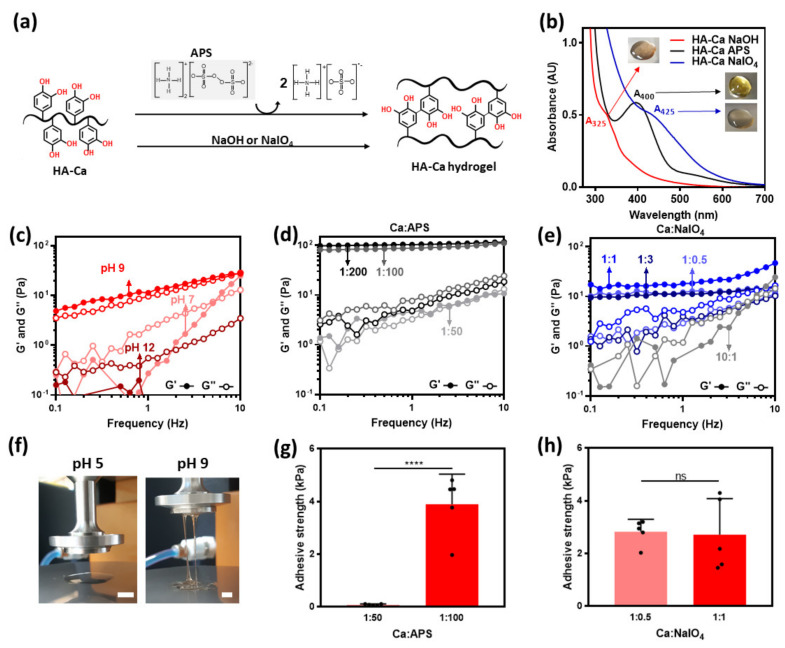
Figure 4.
Adhesive and cohesive properties of chemical oxidants-induced hydrogels. (a) Catechol forms di-catechol covalent bonds owing to APS, NaIO4, NaOH. (b) UV-vis spectra of chemical crosslinking-induced HA–Ca solutions by three different oxidants. Frequency sweep-storage (G′) and loss (G″) moduli of HA–Ca hydrogels at 1% strain, oxidized with (c) NaOH, (d) NaIO4, and (e) APS with different molar ratios of catechol and the oxidant. (f) Images of NaOH-induced hydrogel with different pH (scale bar = 5 mm). Adhesion strength of various oxidants-induced HA–Ca hydrogels on PET substrate in (g) different Ca:APS molar ratio and (h) different Ca:NaIO4 molar ratio (n = 5, mean ± SD) (**** p < 0.0001, ns = not significant).