Figure 3.
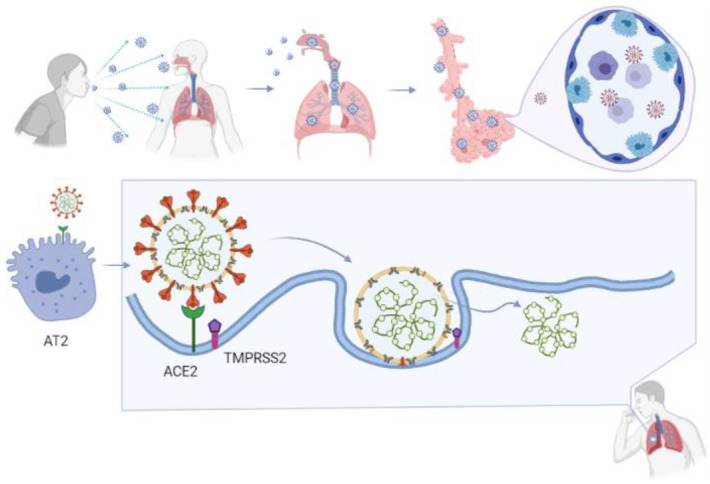
SARS-CoV-2 infection route. Infected COVID-19 patients can spread the virus by sneezing or coughing, or by any other route that drops the infectious particles onto another surface. When a person contracts the virus, the virus recognizes its binding target, ACE2, which is expressed on type II alveolar cells (AT2) in the lower respiratory tract. In the fusion step, the S protein on SARS-CoV-2 binds to ACE2, followed by cleavage of the S glycoprotein-ACE2 complex at polybasic motif (PPAR) at S1/S2 by type 2 transmembrane serine protease (TMPRSS2) and other proteases, leading to conformational alteration and activation of the S-glycoprotein. After fusion with the host cell membrane, the virus releases its genomic material into the cytoplasm.
