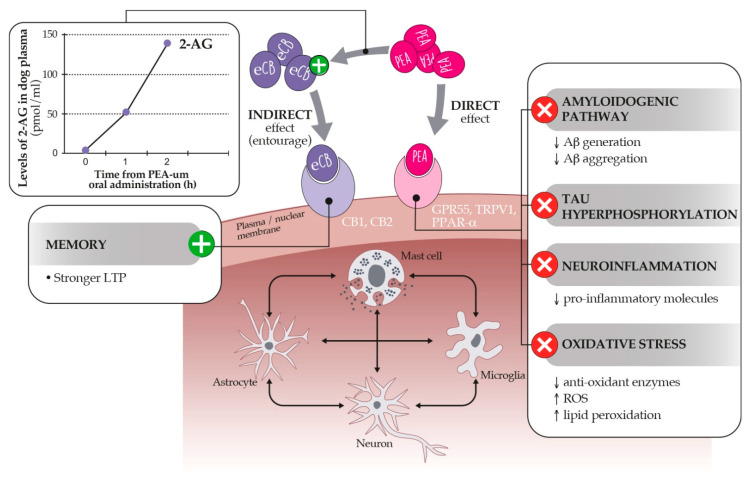
Figure 6.
Proposed mechanisms of action of PEA. PEA exerts a direct and indirect agonism on the endocannabinoidome within brain cells. The direct pathway depends on the activation of GPR55, TRPV1, and PPAR-α receptors, the last inhibiting the hallmarks of age-related cognitive dysfunction (right panel). Through the so-called entourage effect, PEA may also increase the level (left panel) or the binding affinity of endocannabinoids for CB1 and CB2 receptors, favoring stronger LTP (Long Term Potentiation) and memory processes. See text for further details.