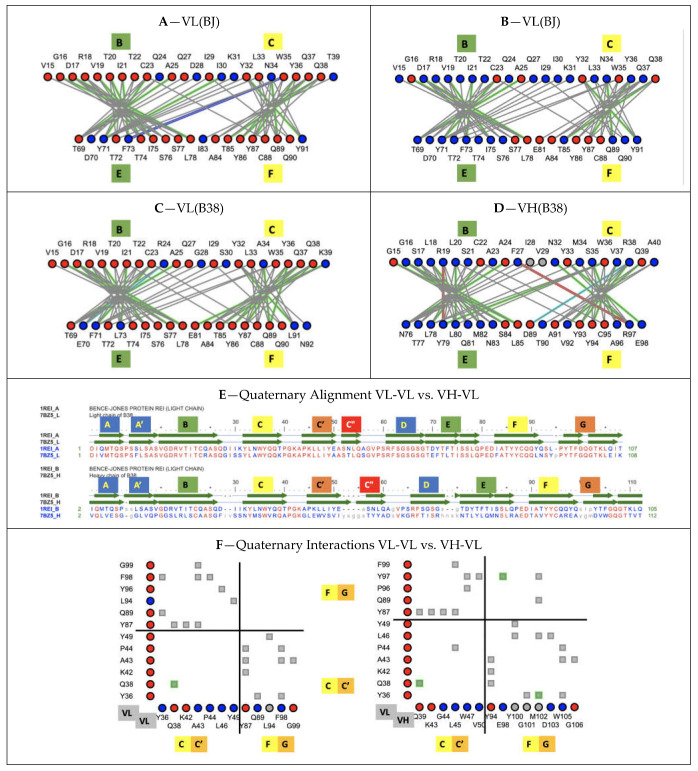
Figure 7.
Interaction networks at the Ig protodomain core interface and quaternary Ig-Ig interface. Comparing protodomain interface BC/EF for (A) B38 Antibody VL domain (7BZ5) (B) B38 Antibody VH domain (C) Bence Jones (BJ) VL domain chainA (1REI) (D) Bence Jones (BJ) VL domain chainB (https://structure.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/icn3d/share.html?i2HiYhm3e4P8ecby6, accessed on 27 August 2021)—residue node colors: red = conserved/blue = not conserved between antibody VH-VL B38 and Bence Jones protein dimer VL-VL. Line colors: interactions: grey = VdW contact; green = H-bond; cyan = charge–charge; red = charge–aromatic; blue = charge–aromatic. Cys bonds shown in grey. The interface exhibits a conserved pattern, including, in particular, the CCW residues. (E) Quaternary Alignment BJ VL-VL vs. B38 VH-VL: the VH-VL dimer (7BZ5) aligns with a VL-VL dimer (1REI) within 1.53 A RMSD over 202 residues with 57% sequence identity. (F) Quaternary interface of BJ homodimer VL-VL (left) vs. B38 heterodimer VH-VL (right) with contributions from protodomain 1 (CC’) and protodomain 2 (FG), forming the GFCC’ sheet (https://structure.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/icn3d/share.html?aYHnSxgAD6kSoQqn8, accessed on 27 August 2021)—colors as in (E)—notice the symmetry in contacts in VL-VL (apart from a small experimental difference) vs. asymmetry in VH-VL, with a highly conserved Q38 vs. Q38/39 H-bonded interaction (green).