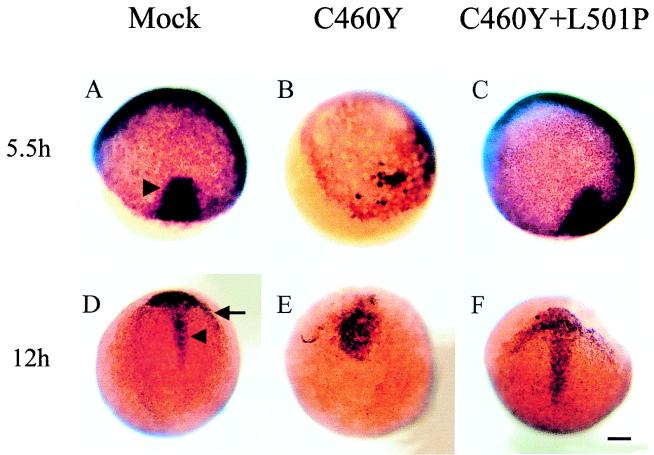
FIG. 10.
Whole-mount in situ hybridization showing the expression of goosecoid in microinjected embryos. Embryos were injected at the one- or two-cell stage with saline (mock) (A and D) or mRNAs encoding the GR DBD (aa 407 to 556) with C460Y (B and E) or C460Y and L501P (C and F) mutations. Patterns of expression of goosecoid at 5.5 h (A to C) and 12 h (D to F) are shown. Dorsal views are shown in panels A, B, and D to F, while an animal pole view is shown in panel C. Injection of GR DBDC460Y/L501P failed to modify gsc expression at all developmental stages (compare panels A, D, C, and F). (A and C) At the onset of gastrulation, gsc is expressed in the embryonic shield on the dorsal part of the embryo (indicated by an arrowhead in panel A). (B) Blastoderm migration in most GRC460Y-injected embryos is delayed compared to that in control embryos and GRC460Y/L501P-injected embryos, and gsc expression is greatly reduced. (D and F) gsc expression is confined to the prechordal plate (indicated by an arrow in panel D) and cells of the anterior part of the dorsal midline (indicated by an arrowhead in panel D). (E) In GRC460Y-injected embryos, gsc is expressed in a cluster of cells without any distinct pattern; in particular, no rostral crescent corresponding to the prechordal mesoderm is visible. Scale bar: A to F, 106 μm.