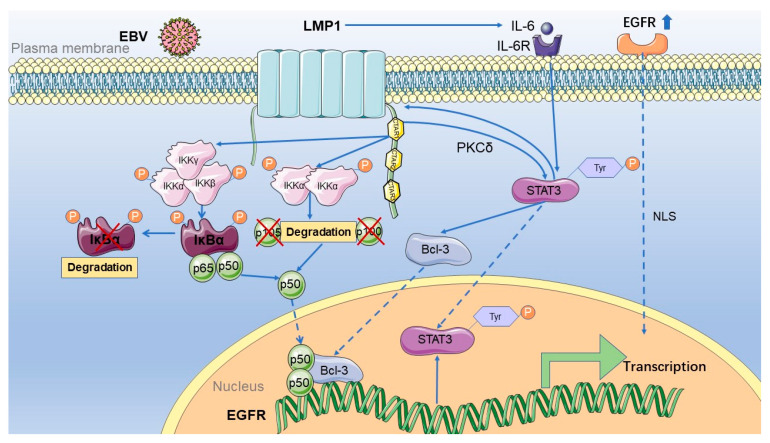
Figure 2.
The mechanism of EGFR activation by LMP1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. LMP1 activates the EGFR mainly in two ways: first, the expression encoded by EBV activates the NF-κB classical and non-classical pathways, and then p50 can enter the nucleus. Meanwhile, LMP1 can regulate the phosphorylation of STAT3 tyrosine 705, which PKCδ mediates. It then activates the expression of Bcl-3 and promotes it to enter the nucleus. Indeed, p50 and Bcl-3 can form a trimer or dimer, binding to the EGFR promoter to activate its transcription. Activated STAT3 can then bind to the LMP1 promoter to regulate the expression of LMP1. At the same time, IL-6 downstream of the NF-κB pathway activated by LMP1 can further activate STAT3 after binding to its receptor. Moreover, STAT3 then binds to the LMP1 promoter to promote the expression of LMP1, forming a positive autoregulatory loop. STAT3 is not only regulated by LMP1 but also regulated by the activation of EGFR. IKKα, IkappaB kinase-alpha; IKKβ, IkappaB kinase-beta; IKKγ, IkappaB kinase-gamma; IκBα, IkappaBalpha; LMP1, latent membrane protein 1; EBV, Epstein–Barr virus; Bcl-3, B-cell lymphoma 3; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; NLS, nuclear localization protein; CTAR, carboxyl-terminal activating regions; IL-6, interleukin 6; IL-6R, interleukin 6 receptor.