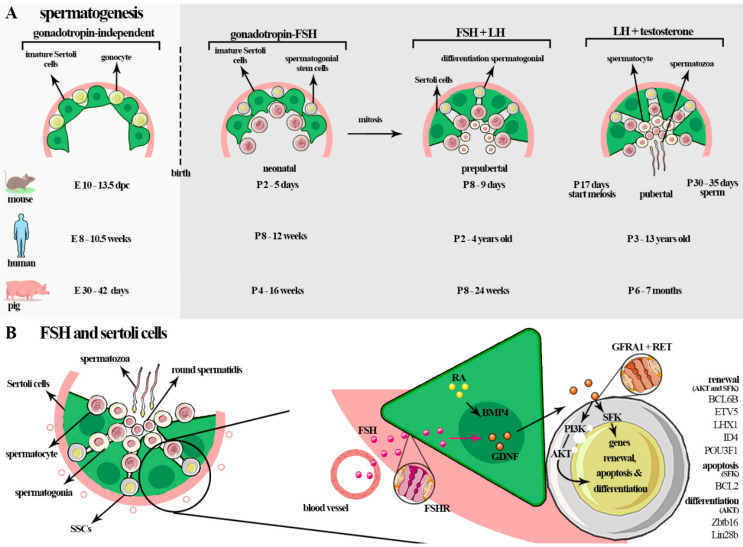
Figure 3.
(A) In fetal life, PGCs transform into gonocytes that remain centrally placed, surrounded by immature Sertoli cells. In mice, gonocyte development occurs before the formation at E10-13.5 d.p.c, in humans at E 8–10.5 weeks, and in pigs at E30–42 d.p.c (gonadotropin-independent). In the neonatal phase, FSH, through FSHR signaling, regulates the proliferation of the cells and the number of cells that will be had in adult life (~P2–5-day mice (postpartum), ~P8–12 weeks in humans, and ~P4–16 weeks in pigs). During the prepubertal phase, an increase in FSH occurs during the maturation of Sertoli cells and during the completion of the first cycle of sperm (~P8–10 days in mice; ~P2–4 years in humans; ~P8–24 weeks in pigs). In adult life, the spermatogenesis process starts. This is a complex process in which diploid spermatogonia self-renew, proliferate, and differentiate into haploid spermatozoa. The gonadotropins act in the early events of the spermatogenesis, before spermiogenesis, mainly in spermatogonial proliferation and meiosis. These hormones act on all phases of spermatogenesis in some species such as rodents and a specific phase of spermatogenesis in men: the maturation of type A spermatogonia to type B spermatogonia, meiosis, and spermiation. (B) In germ cells, FSH mainly influences self-renewal, proliferation, and survival of spermatogonia cells through glial cell-line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) secreted by Sertoli cells. Sertoli cells secrete many factors linked to self-renewal such as GDNF and fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2), differentiation and proliferation of spermatogonial stem cells (SSCs), bone morphogenetic protein (BMP4), and activin A, amongst others such as KIT ligand (KL or stem cell factor—SCF), which promotes the KIT tyrosine-kinase receptor expressed by differentiated spermatogonia. GDNF induces SSC self-renew and survival through multiple pathways such as AKT/MEK, AKT, and SFK. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT pathway influences the self-renewing divisions of SSCs, inhibits apoptosis, and is involved in activating mTORC1 through the SFK signaling pathway. GDNF upregulates the specific SSC genes such as B cell CLL/lymphoma 6, member B (BCL6B), Ets variant gene 5 (ETV5), and Lim homeobox protein 1 (LHX1). GDNF also acts on the canonical RAS/ERK1/2 pathway, important for the proliferation and self-renewal of these cells by phosphorylation and activation of CREB1, ATF1, CREM, and c-FOS factors.