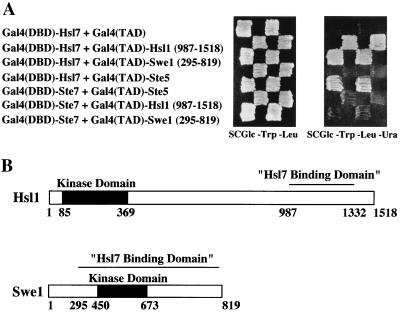
FIG. 3.
A two-hybrid screen identifies both Hsl1 and Swe1 as Hsl7-interacting proteins. (A) A reporter strain (YD116) in which URA3 expression is GAL1 promoter dependent was cotransformed with a plasmid expressing a Gal4(DBD)-Hsl7 chimera and plasmids expressing either Gal4(TAD) alone (top row), Gal4(TAD)-Hsl1(987-1518) (second row), Gal4(TAD)-Swe1(295-819) (third row), or, as an additional negative control, Gal4(TAD)-Ste5 (fourth row). The same strain was cotransformed with a plasmid expressing Gal4(DBD)-Ste7 and plasmids expressing, as a positive control, either Gal4(TAD)-Ste5 (fifth row), Gal4(TAD)-Hsl1(987-1518) (sixth row), or Gal4(TAD)-Swe1(295-819) (last row) to demonstrate specificity. (B) Schematic diagrams of the primary structure of the Hsl1 and Swe1 protein kinases. Catalytic domain (solid box), noncatalytic regions (open boxes), and the minimal Hsl7-binding domain (overlined) in each protein, as delineated by the smallest common segment shared by the corresponding clones isolated in the two-hybrid screen, and their relative sequence positions (numbers below) are indicated.