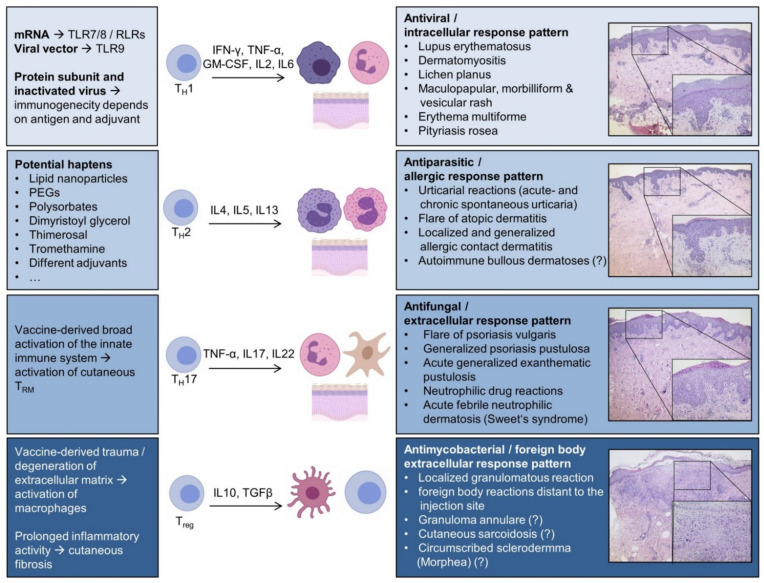
Figure 3.
The mode of action varies among the different vaccine types, but it ultimately leads to increased expression of IFN-γ, which is a prerequisite for sufficient antiviral immunogenicity. Notably, mRNA and viral vector vaccines activate different TLRs; therefore, immunological differences appear plausible [36,37]. Moreover, vaccines comprise various molecules that potentially act as haptens to elicit type IV allergic reactions [38]. At this point, it is not clear whether specific vaccine types impose a larger risk for severe cutaneous ADRs to specific groups of patients, e.g., psoriatic patients. A dysregulation of regulatory T cells may shift macrophages to initiate granulomatous reactions, and longstanding inflammatory activity might induce fibrogenic alterations of the dermis to result in circumscribed scleroderma (morphea). Abbreviations: TLR—Toll-like receptor; RLR—RIG-I-like receptors; TRM—Tissue-resident memory T cell; PEG—polyethylene glycol. This immunological scheme is adapted from [35].