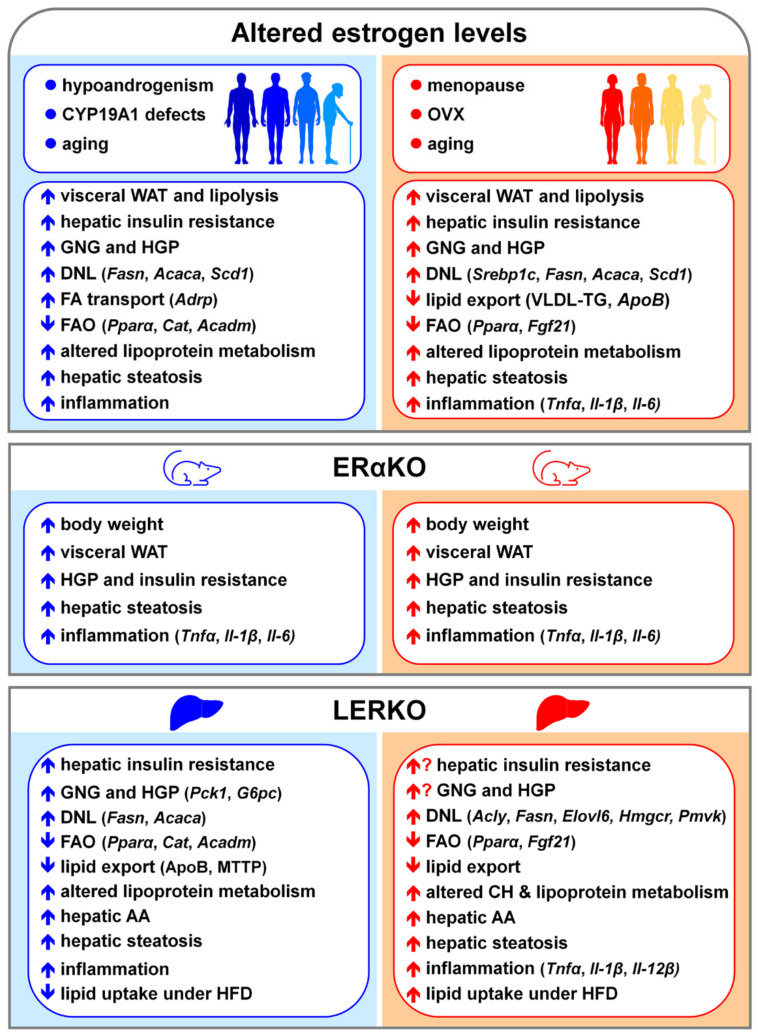
Figure 5.
Consequences of altered estrogen signaling in the liver of males (left, in blue) and females (right, in red) favoring NAFLD development and progression. Abbreviations: AA, amino acids; Acaca, acetyl-CoA carboxylase α; Acadm, acyl-CoA dehydrogenase medium chain; Acly, ATP citrate lyase; Adrp, adipocyte differentiated regulatory protein; ApoB; apolipoprotein B; Cat, catalase; CH, cholesterol; CYP19A1, aromatase; DNL, de novo lipogenesis; Elovl6, ELOVL fatty acid elongase 6; ERαKO, total ERα knockout mice; FA, fatty acids; FAO, fatty acid oxidation; Fasn, fatty acid synthase; Fgf21, fibroblast growth factor 21; G6pc, glucose-6-phosphatase; GNG, gluconeogenesis; HFD, high fat diet; HGP, hepatic glucose production; Hmgcr, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase; Il-1β, interleukin 1β; Il-6, interleukin 6; Il-12β, interleukin 12β; LERKO, liver ERα knockout mice; MTTP; microsomal triglyceride transfer protein; OVX, ovariectomy; Pck1, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 1; Pmvk, phosphomevalonate kinase; Pparα, peroxisome proliferator activated receptor α; Scd1, stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1; Srebp1c, sterol regulatory element binding Transcription factor 1; Tnfα, tumor necrosis factor α; VLDL-TG, very-low density lipoprotein-triglycerides; WAT, white adipose tissue.