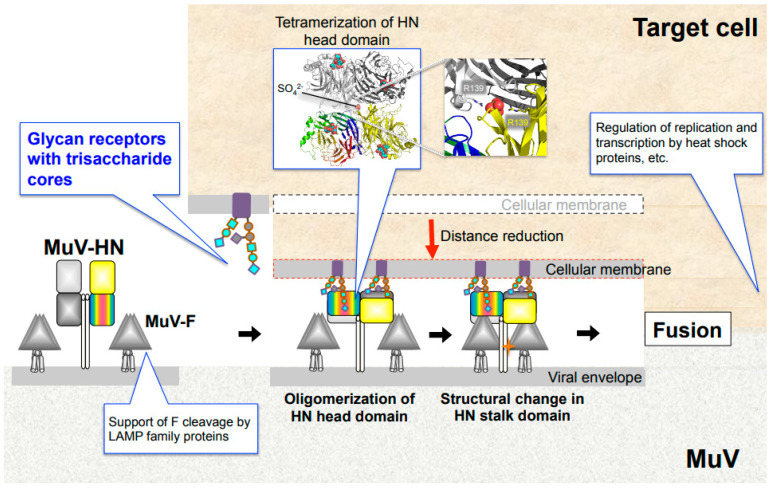
Figure 3.
MuV entry mechanism and host factors. Binding of MuV-HN to glycan receptors causes sequential conformational changes in the HN and F proteins, leading to membrane fusion. Multimerization of the MuV-HN head domain upon receptor binding may affect the structural change of the MuV-HN stalk domain, which in turn may trigger the structural change of the F protein. Following cellular entry, replication and transcription of the viral genome are regulated by host factors, such as heat shock protein family. LAMP family proteins support furin-mediated cleavage of the newly synthesized F protein.