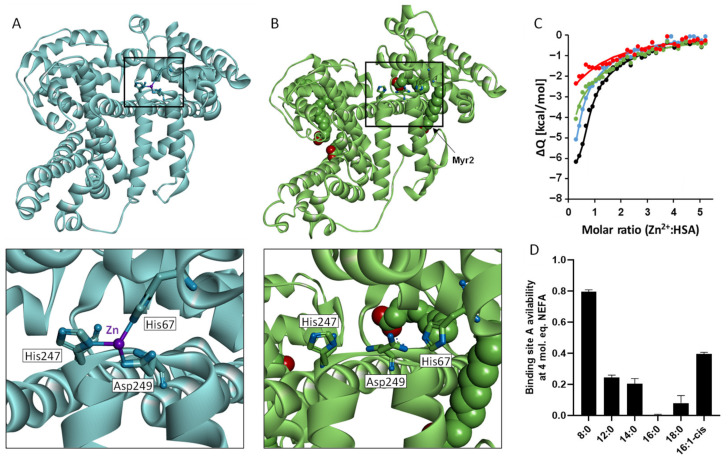
Figure 2.
Influence of fatty acids on HSA structure and zinc binding. (A). X-ray crystal structure of HSA with zinc bound (PDB: 5IJF). Zinc binds in a tetrahedral geometry at site A involving the side chains of His67, His247, and Asp249. (B). X-ray crystal structure of HSA with myristate bound (PDB: 1BJ5). The binding of myristate at the FA2 site causes movement of zinc-binding residue His67 away from His247 and Asp249. (C). Isothermal titration calorimetry showing the effect of fatty acid loading on zinc binding to HSA. In the experiments 1.5 mM ZnCl2 was titrated into 60 µM HSA, in the presence of either 0 (black), 3 (blue), 4 (green), or 5 (red) mol. eq. of myristate in a buffer containing 50 mM Tris, 140 mM NaCl, pH 7.4. (D). Bar chart representing the availability of binding site A in the presence of 4 mol. eq. of various fatty acids. All except octanoate had large effects on Zn2+ binding to the protein. Data for parts C and D were taken from Sobczak et al. [88].