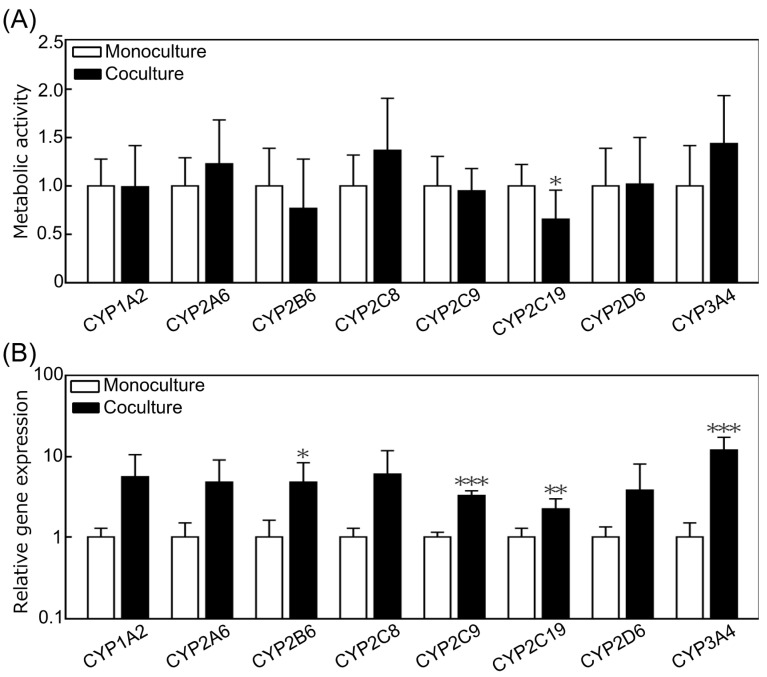
Figure 5.
Evaluation of the coculture effects on the metabolic function of primary hepatocytes derived from chimeric mice with humanized liver tissues (PXB cells). (A) Metabolic activity of PXB cells normalized by monoculture using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). The metabolic activity of CYP2C19 was significantly decreased by coculture (n = 5–8). (B) The relative gene expression levels related to the metabolism of PXB cells tended to increase in coculture. Significant differences were observed in the expression levels of CYP2B6, 2C9, 2C19, and 3A4 (n = 7–18). Each value was normalized to that of the monoculture for each gene. Data represent the mean ± SD, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.005.