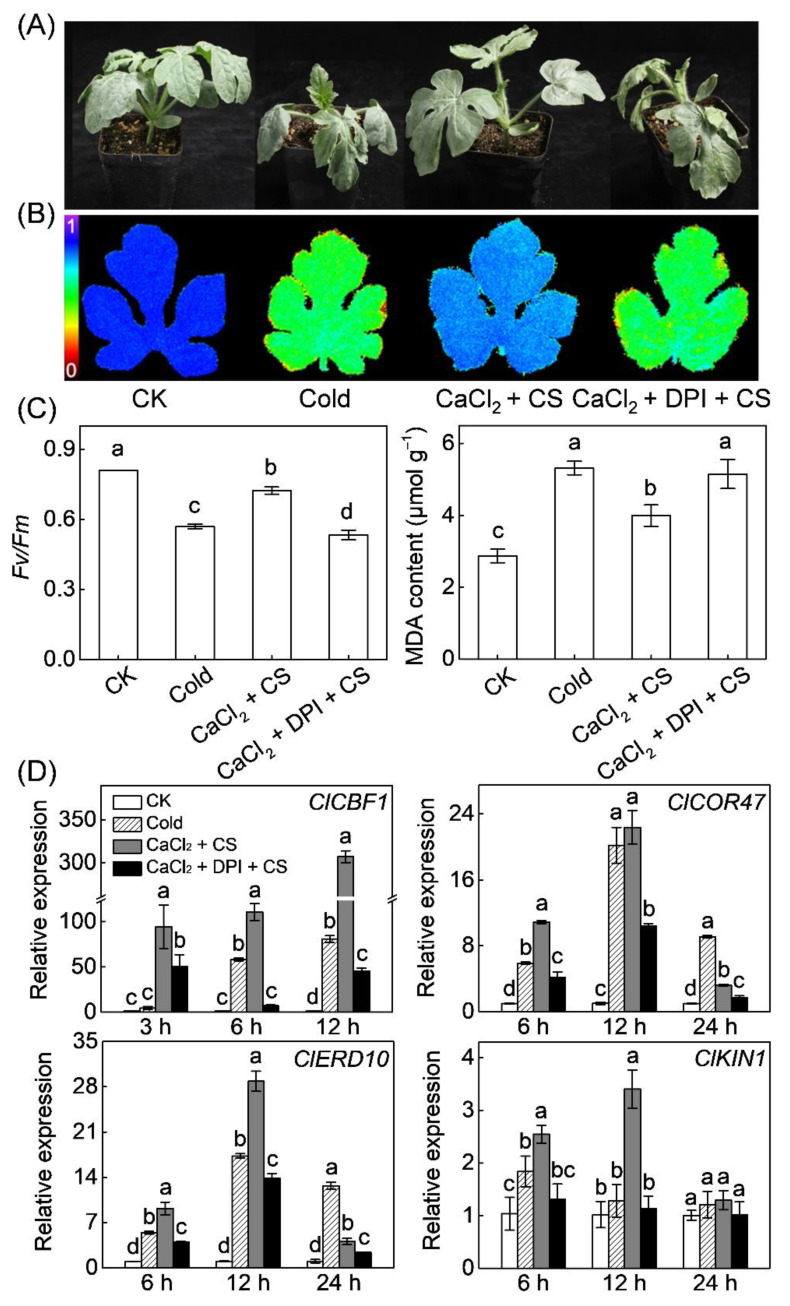
Figure 5.
The role of H2O2 in CaCl2-induced C-REPEAT BINDING FACTOR (CBF) pathway and chilling tolerance in watermelon. (A) Chilling phenotypes. (B) Images showing the maximum PSII quantum yield (Fv/Fm). The false-color code depicted at the left of the image ranges from 0 (black) to 1 (purple). (C) The average values of Fv/Fm and malondialdehyde (MDA) contents. (D) The expression of ClCBF1 and its regulons, including cold-responsive gene 47 (ClCOR47), early responsive to dehydration 10 (ClERD10), and cold induced gene 1 (ClKIN1). The plant leaves were sprayed with 20 mM CaCl2 for 12 h and then exposed to cold stress (CS) at 4 °C. To inhibit H2O2 production, the seedlings were pretreated with 100 µM DPI 2 h before CaCl2 application. Seedlings sprayed with distilled water under temperatures of 28/18 °C (day/night) were set as control (CK). Relative expression of genes in CK plants was set as 1.0. Data show the means of three replicates ± standard deviation (SD). The different letters denote significant difference at p < 0.05 according to Turkey’s test.