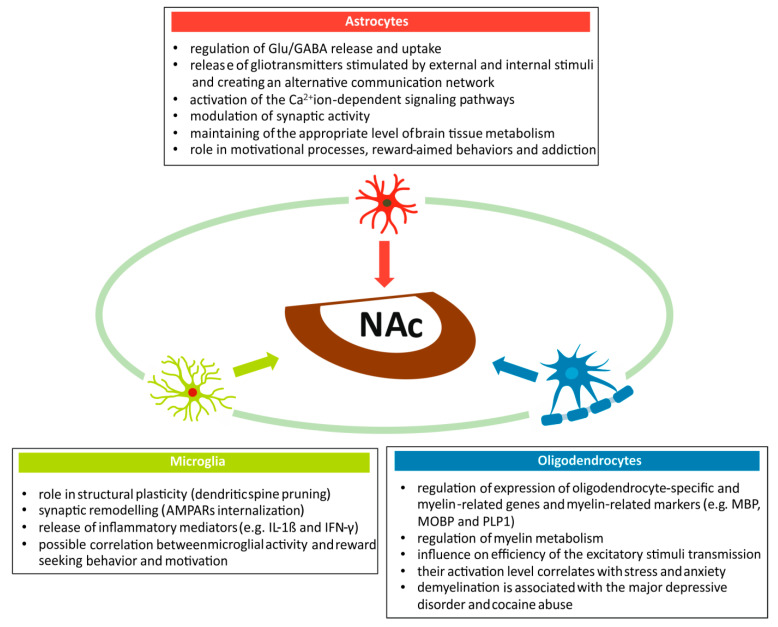
Figure 4.
Neuroglia function in nucleus accumbens. Neuroglial cells play an important function in the regulation of not only physiological but also pathological processes in NAc. The role of astrocytes is maintenance of the signaling pathways through providing NAc with neurotransmitters, modulation of synaptic activity, and establishing an alternative communication network due to secreted gliotransmitters. In addition, astrocytes are responsible for maintaining an appropriate level of brain tissue metabolism. Microglia, through release of the inflammatory mediators, influence morphological and functional neuroplasticity and modulate neuronal activity. Oligodendrocytes are involved in regulation of the expression of the myelin metabolism-related genes. Consequently, through maintaining the transmission efficiency of excitatory stimuli along the nerve fibers, these cells have the potential to influence activity and plasticity processes in the BRS. All neuroglial cell subpopulations play an important role in the pathological processes affecting the NAc integrity, although their contribution to these processes is still poorly understood.