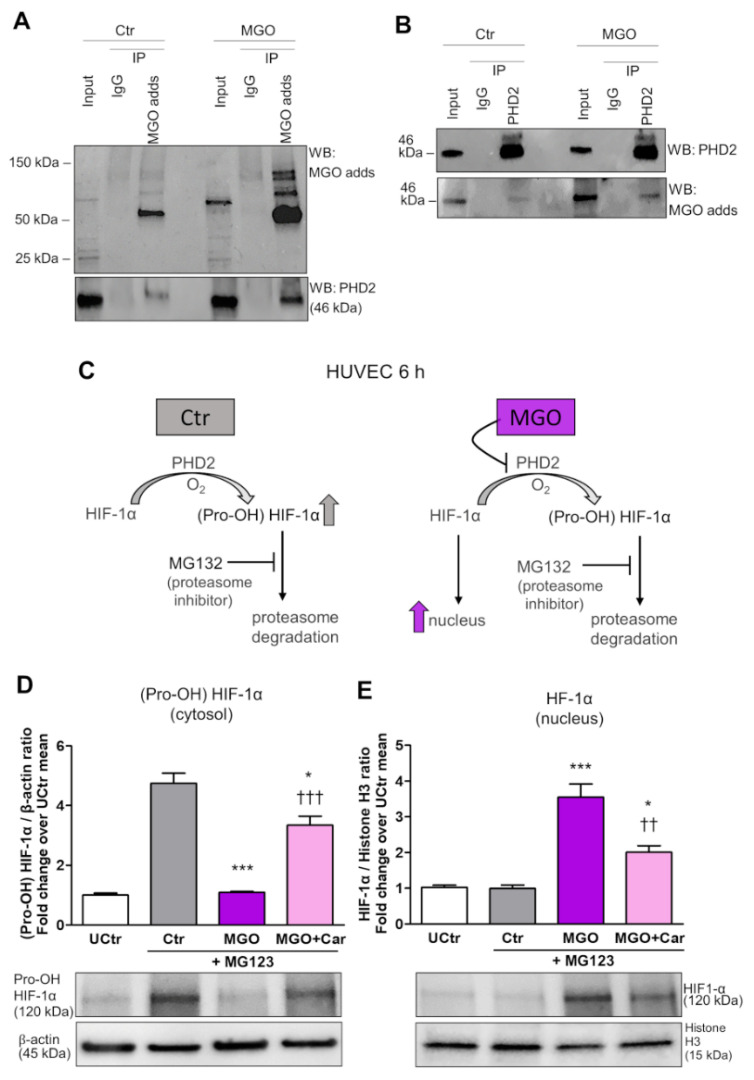
Figure 4.
The glycolytic side-product MGO activates nuclear translocation of HIF-1α by inducing post-translational glycation and inhibition of PHD2 activity. IP of MGO-protein adducts (MGO adds) (A) or PHD2 (B) on HUVEC treated (MGO) or not (Ctr) with 200 µM MGO for 6 h, using a specific antibody for MGO modified proteins (A) or a specific anti-PHD2 antibody (B), respectively. Mouse IgG were used as control. Total cell lysates (Input) and immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted for PHD2 and MGO protein adducts (A,B). In the presence of oxygen, HIF-1α is rapidly hydroxylated by PHD2 to generate (Pro-OH) HIF-1α, which is degraded through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway; proteasome inhibition with MG132 led to Pro-OH HIF-1α increase, and adding MGO prevented (Pro-OH) HIF-1α increase and led to HIF-1α nuclear translocation (C). Western blot analysis for (Pro-OH) HIF-1α in total extracts (D), and non-hydroxylated HIF-1α in nuclear extracts (E) from HUVEC, treated or untreated (UCtr) with the proteasome inhibitor MG132 (10µM) for 6 h, with or without MGO, in the presence or absence of Car. Bars represent mean ± SEM. Post hoc multiple comparison: *** p < 0.001 or * p < 0.05 vs. Ctr; ††† p < 0.001 or †† p < 0.01 vs. MGO.