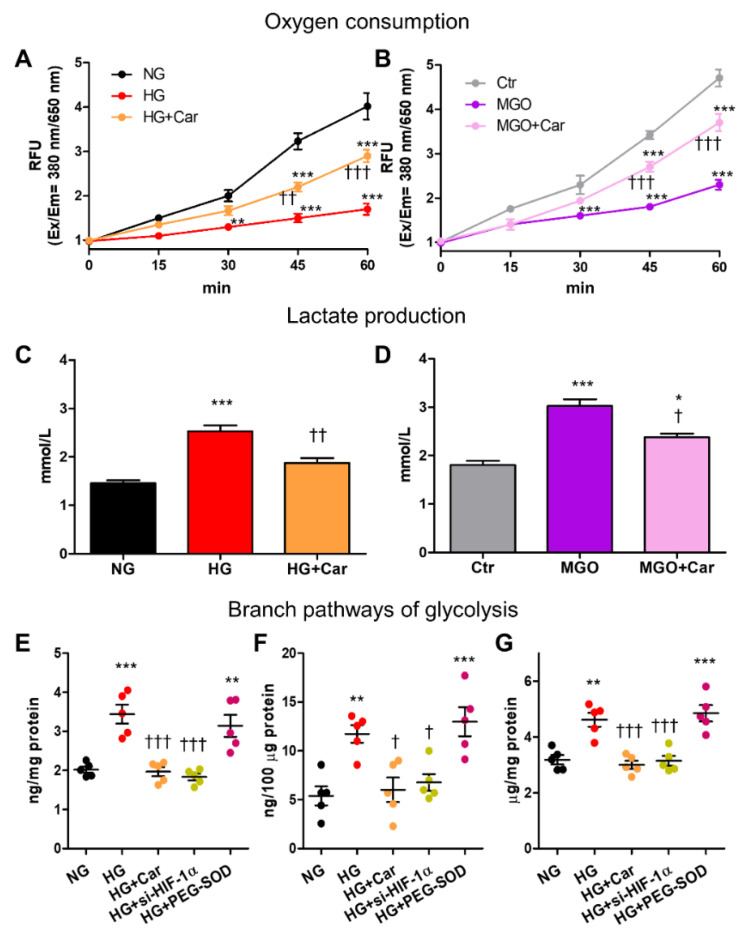
Figure 6.
HG and the glycolytic side product MGO induce cellular energetic changes that resemble the Warburg effect and are associated with the activation of the alternative pathological pathways of glucose metabolism in HG conditions. Time course of oxygen consumption (A,B) and lactate production at 48 h (C,D) by HUVEC exposed to HG (20 mM) vs. NG (5.5 mM) (A,C), or treated with MGO (200 µM) vs. untreated cells (Ctr) (B,D), with or without the carbonyl trapping agent Car (20 mM); n = 3 separate experiments in duplicate per condition. Hexosamine (E), polyol (F) and AGE (G) pathways activation in HUVEC exposed to HG vs. NG for 48 h, with or without Car, as determined by measuring the levels of GFPT1 (E), D-sorbitol (F), and AGEs (G); each dot represents the mean of two technical replicates of 5 wells per condition. Bars represent mean ± SEM. Post hoc multiple comparison: *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01 or * p < 0.05 vs. NG or Ctr (as appropriate); ††† p < 0.001, †† p < 0.01 or † p < 0.05 vs. HG or MGO (as appropriate).