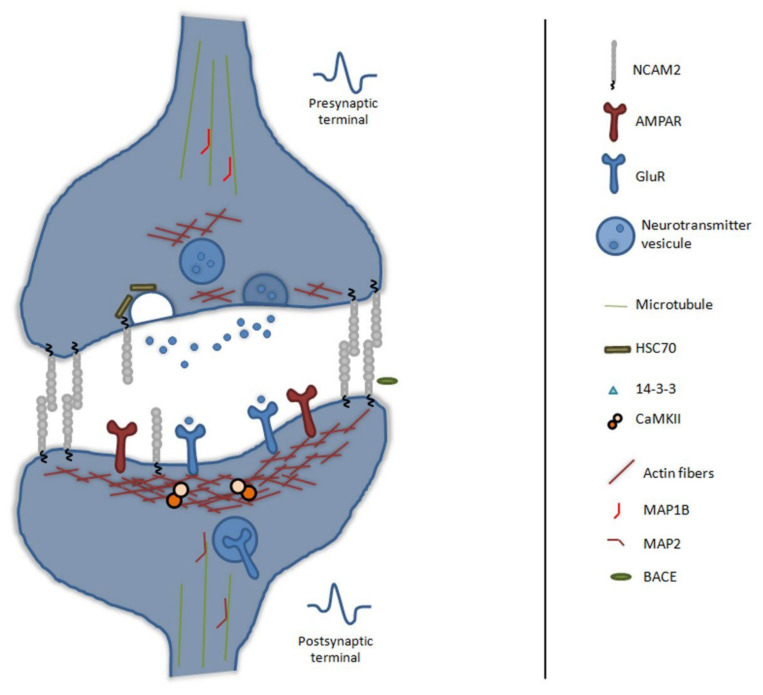
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of NCAM2 functions and interactions in synapse maintenance and plasticity. NCAM2 is involved in synapses formation, it is detected in the presynaptic and postsynaptic compartments and undergoes trans-homophilic binding between both compartments. NCAM2 interacts with different scaffold proteins or complexes, which control the shape and dynamics of synapses; such as CaMKII, Actin, 14-3-3 or CAPZ. NCAM2 is involved in synaptic transmission through the neurotransmitters vesicles recycling pathway and the amount of glutamate receptors. Proteolytic cleavage of NCAM2 by BACE1 is important for synapse plasticity and remodeling. Beta-site APP cleaving enzyme 1, BACE1; Microtubule associated protein 1B, MAP1B; Microtubule associated protein 2, MAP2; Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type II, CaMKII; F-actin-capping protein, CAPZ; α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor, AMPAR; glutamate receptor, GluR and Heat shock cognate 71 kDa, HSC70.