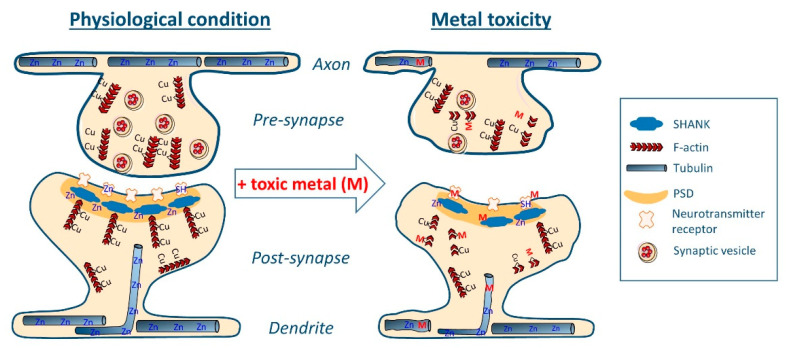
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of synaptic toxicity mechanisms by direct competition of toxic metals (M) with physiological metal binding sites (Cu, Zn) within cytoskeletal proteins (e.g., tubulin, F-actin and/or F-actin binding proteins), PSD scaffold proteins (e.g., SHANK), and neurotransmitter receptors (e.g., NMDAR). These metal–protein interactions can damage the synaptic structure and lead to loss of connectivity between neurons.