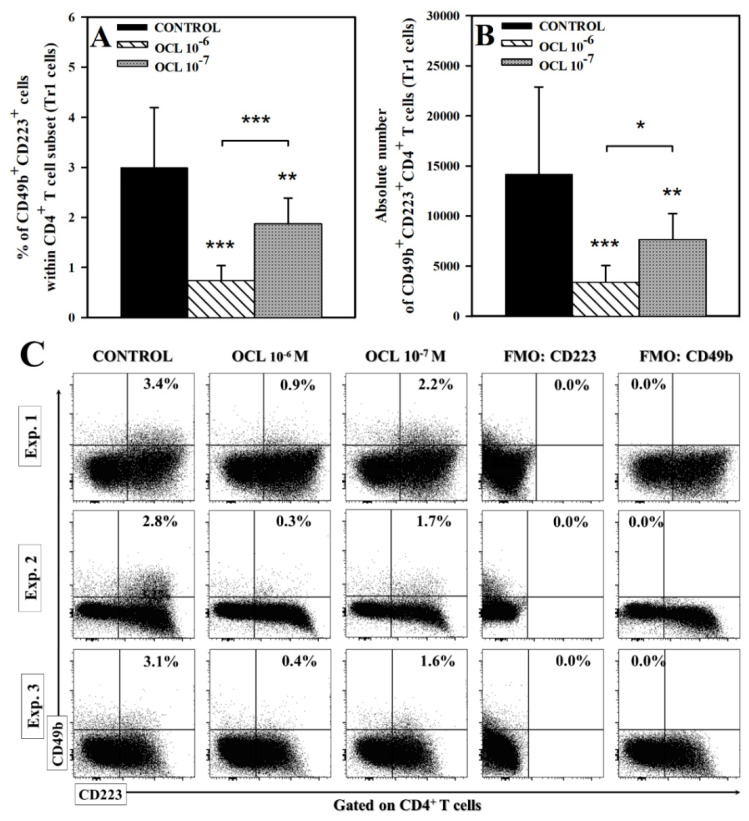
Figure 5.
Effect of oclacitinib (OCL) on the number of CD49b+CD223+CD4+ T cells. The relative (A) and absolute count (B) of CD49b+CD223+CD4+ cells were determined in cell cultures incubated with or without (control) OCL (10−6 M and 10−7 M). The relative count is expressed as a percentage of CD49b+CD223+ cells within CD4+ T cell subset. The absolute count represents the number of CD49b+CD223+CD4+ T cells per sample well. Cells with such a phenotype should be equated with Tr1 cells. Results are expressed as the mean (±S.D.) of three independent experiments with 5 mice per experiment (overall n = 15, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, control cells vs OCL-treated (10−6 or 10−7 M) cells (Student’s unpaired t-test), or OCL 10−6-treated vs OCL-10−7-treated cells (one way ANOVA with Holm-Sidak multiple comparison test)). Examples of dot plot cytograms show the distribution of CD49b+CD223+ cells among CD4+ T cell subset (C). Fluorescence minus one (FMO) controls were applied to confirm the gating strategy used to identify CD49b+CD223+ cells.