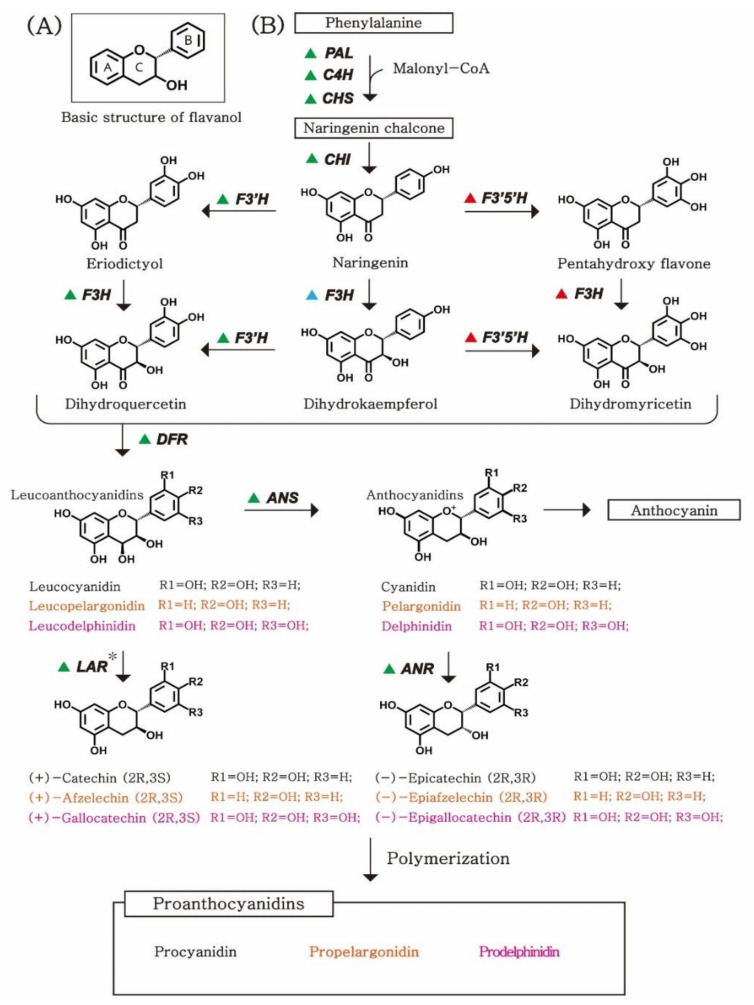
Figure 1.
Biosynthetic pathway of PAs: (A) Basic chemical structure of flavan-3-ols. Flavan-3-ols have two benzene rings and one heterocyclic benzopyran ring. (B) A schematic diagram with chemical structures of flavanol compounds. Triangles indicate the species-specific enzymes involved in each biosynthetic pathway. The green triangle shows the enzymes that exist in all of our target species (Table 1); exceptionally, the LAR* gene, which catalyzes (2R, 3S)-flavanols such as catechin, was not identified in A. thaliana. A blue or red triangle indicates the enzyme that is present in grape, blueberry, and tea plant, or strawberry and almond, respectively. The names of the metabolites have been colored based on their hydroxyl pattern on the B-ring, and the black, orange, and pink designate 3′4′-dihydroxyl, 4′-hydroxyl, and 4′5′6′-trihydroxyl patterns, respectively. PAs: proanthocyanidins; ANR: anthocyanidin reductase; ANS: anthocyanidin synthase; LAR: leucoanthocyanidin reductase; F3′H: flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase; F3′5′H: flavonoid 3′,5′-hydroxylase; DFR: dihydroflavonol.