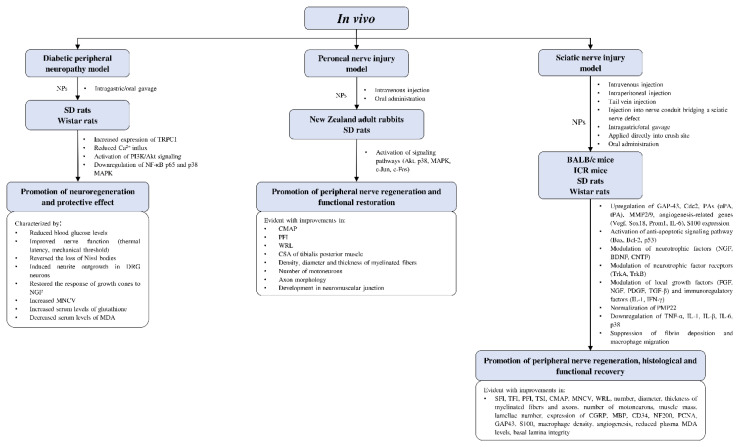
Figure 5.
Overview of in vivo studies that demonstrated the effects of natural products relating to peripheral nerve regeneration across different experimental models with associated mechanisms. Akt—protein kinase B; Bax—Bcl-2-associated X protein; Bcl-2—B-cell lymphoma 2; BDNF—brain-derived neurotrophic factor; Cdc2—cell division control protein; CGRP—calcitonin gene-related peptide; CMAP—compound muscle action potential; CNTF—ciliary neurotrophic factor; CSA—cross-sectional area; DRG—dorsal root ganglion; FGF—fibroblast growth factor; GAP-43—growth associated protein 43; ICR—Institute of Cancer Research; IFN-γ—interferon-γ; IL—interleukin; MAPK—mitogen-activated protein kinase; MBP—myelin basic protein; MDA—malondialdehyde; MMP2/9—matrix-metalloproteinase-2/9; MNCV—motor nerve conduction velocity; NF-κB—nuclear factor kappa B; NGF—nerve growth factor; NPs—natural products; PAs—plasminogen activators; PCNA—proliferating cell nuclear antigen; PDGF—platelet-derived growth factor; PFI—peroneal function index; PI3K—phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PMP22—peripheral myelin protein 22; Prom1—prominin 1; SD—Sprague-Dawley; SFI—sciatic function index; Sox18—sex-determining region Y-box transcription factor 18; TFI—tibial function index; TGF-β—transforming growth factor-β; TNF-α—tumor necrosis factor-α; tPA—tissue plasminogen activator; Trk—tropomyosin receptor kinase; TRPC1—transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily C member 1; TSI—toe spread index; uPA—urokinase plasminogen activator; Vegf—vascular endothelial growth factor; WRL—withdrawal reflex latency.