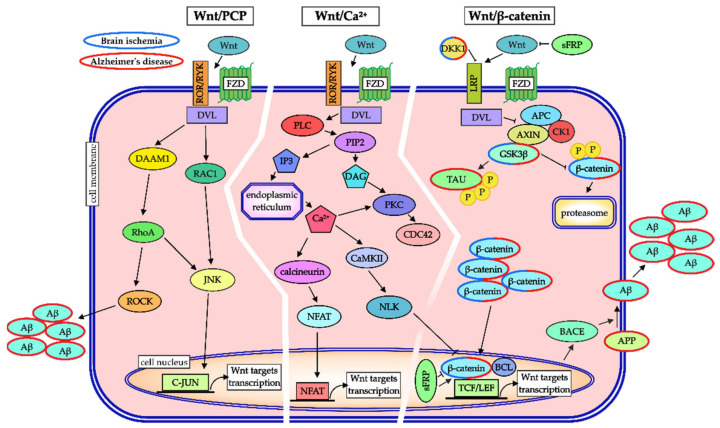
Figure 2.
Participation of Wnt signaling in ischemic brain injury and Alzheimer’s disease. The scheme depicts three Wnt signaling pathways: two non-canonical branches, the planar cell polarity (Wnt/PCP) pathway and the Wnt/calcium (Ca2+) pathway, and the canonical, Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Wnt signaling is implicated in several processes associated with brain ischemia (indicated by blue outlines of the proteins) and Alzheimer’s disease (indicated by red outlines of the proteins). For more information, please refer to the main text. Abbreviations: Aβ, amyloid β; APC, adenomatous polyposis coli; APP, amyloid precursor protein; AXIN, axis inhibition; BACE, β-site APP-cleaving enzyme 1; BCL, B-cell lymphoma; C-JUN, transcription factor C-JUN; CaMKII, Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II; CDC42, GTPase CDC42; CK1, casein kinase 1; DAAM1, DVL-associated activator of morphogenesis 1; DAG, diacylglycerol; DKK1, dickkopf 1; DVL, disheveled; FZD, frizzled receptor; GSK3β, glycogen synthase kinase 3β; IP3, inositol trisphosphate; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; LRP, low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein receptor; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T-cells; NLK, nemo-like kinase; P, phosphorylation; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; PKC, protein kinase C; PLC, phospholipase C; RAC1, Rac family small GTPase 1; RhoA, small GTPase Ras homolog family member A; ROCK, Rho-associated kinase; ROR/RYK, tyrosine kinase receptors RYK/ROR; sFRP, secreted frizzled-related protein; TCF/LEF, transcription factors T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer-binding factor; Wnt, Wnt protein/ligand.