FIG. 4.
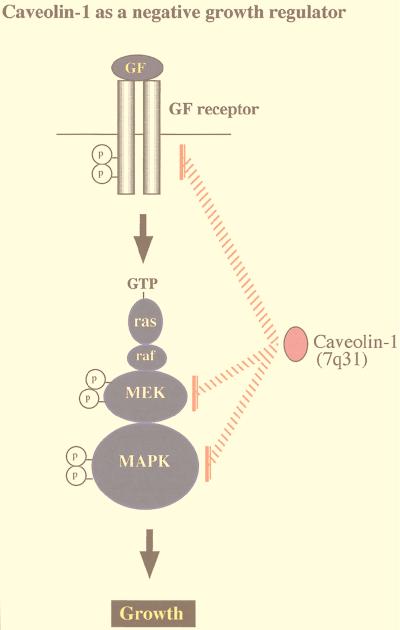
Caveolins negatively regulate signaling along the p42/44 MAPK cascade. Caveolae have been implicated in signaling through the p42/44 MAPK pathway. Caveolin-1 can inhibit signal transduction from the p42/44 MAPK cascade both in vitro and in vivo by acting as a natural endogenous inhibitor of EGF-R, MEK, and ERK (31). Conversely, when NIH 3T3 cells are used, antisense-mediated reductions in caveolin-1 protein expression are sufficient to constitutively activate the p42/44 MAPK cascade and drive oncogenic transformation (49). In normal NIH 3T3 cells, caveolin-1 expression levels are downregulated in rapidly dividing cells and dramatically upregulated at confluency. Thus, upregulation of caveolin-1 expression levels may be important in mediating normal contact inhibition and in negatively regulating the activation state of the p42/44 MAPK cascade. In accordance with these findings, the caveolin-1 gene is localized to a suspected tumor suppressor locus that is deleted in many forms of human cancer (7q31.1/D7S 522 locus) (34, 36).