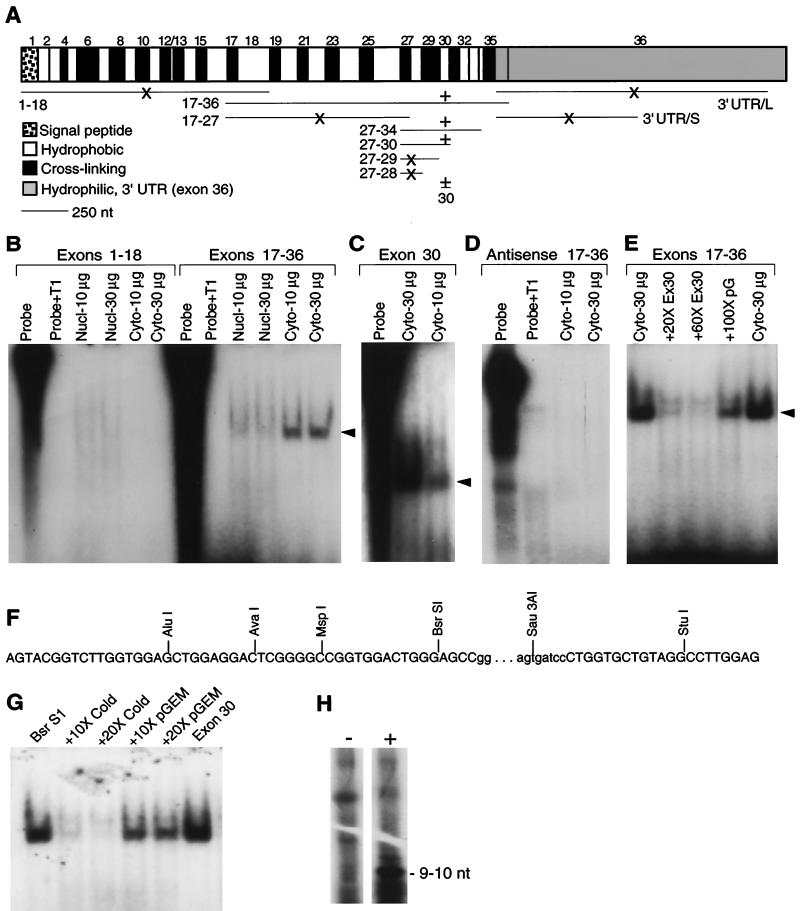
FIG. 3.
Sequences in exon 30 bind a cytosolic factor present in adult lung fibroblasts. (A) Map of tropoelastin mRNA and summary of the binding data. Tropoelastin mRNA is transcribed from 36 exons, which alternate between regions coding for hydrophobic or cross-linking domains. Exon 36 codes for a conserved hydrophilic domain and the fairly large 3′ UTR. The horizontal lines under the mRNA map indicate the RNA probes used protection assays; the numbers designate which exons the probes represent. For exon 36, two probes were made: 3′ UTR/L include all of the exon-36 sequences up to the first polyadenylation signal; 3′ UTR/S is a truncated version of 3′ UTR/L. +, Protected band was detected; ×, no detectable binding. (B) 32P-labeled RNA probes were transcribed in vitro and incubated with fixed amounts (10 or 30 μg of total protein) of nuclear or cytosolic extracts from adult lung fibroblasts. After a 30-min incubation, unbound RNA was digested by T1 RNase, and protected products were resolved by electrophoresis and visualized by autoradiography. No protected fragment or residual probe was seen in reactions containing T1 RNase without cytosolic extract (Probe+T1). A protected band (arrowhead) was produced with an RNA probe covering exons 17 to 36 incubated with cytosolic extract (Cyto) but not when incubated with nuclear extracts (Nucl). In contrast, no protected band was detected with an RNA probe covering exons 1 to 18. (C) A protected band was detected with exon-30 RNA and cytosolic extract. Because gels were not all the same dimension or run for the same time, the migration of the protected band differs among experiments. (D) No protected bands were detected with antisense RNA probes. (E) Yield of the protected band produced with RNA probe 17-36 was inhibited with a 20- or 60-fold excess of unlabeled exon 30 RNA (Ex30). Unlabeled RNA transcribed from pGEM plasmid sequences (pG) did not inhibited production of the protected band. (F) Sequence of rat tropoelastin exon 30. The bases in lowercase letters represent a 72-bp insert found only in the rodent gene. Progressively smaller 32P-labeled RNA probes were transcribed from insert linearized with the indicated restriction enzymes and were incubated with adult fibroblast cytosolic extract. All probes produced the same protected fragment, and an example is shown in the next panel. (G) Incubating 32P-labeled RNA probe transcribed from BsrSI-linearized exon-30 cDNA with 30 μg of cytosolic extract from adult lung fibroblasts produced a protected fragment. The size of the protected fragment was identical to that produced with a full-length exon-30 RNA probe. Binding was specifically competed with excess cold exon-30 RNA but not with RNA transcribed from pGEM plasmid sequences. (H) RNA probe 27-34 was incubated with (+) or without (−) adult fibroblast cytosolic extract before addition of T1 RNase. The protected products were resolved by electrophoresis, excised from the gel, and extracted in phenol-chloroform. The resulting 32P-labeled RNA fragment was resolved on a sequencing gel, and its size was determined by comparison to the migration of single-stranded DNA markers. One prominent band migrating at ca. 9 to 11 nt was detected. Other bands common to both lanes likely represent undigested RNA.