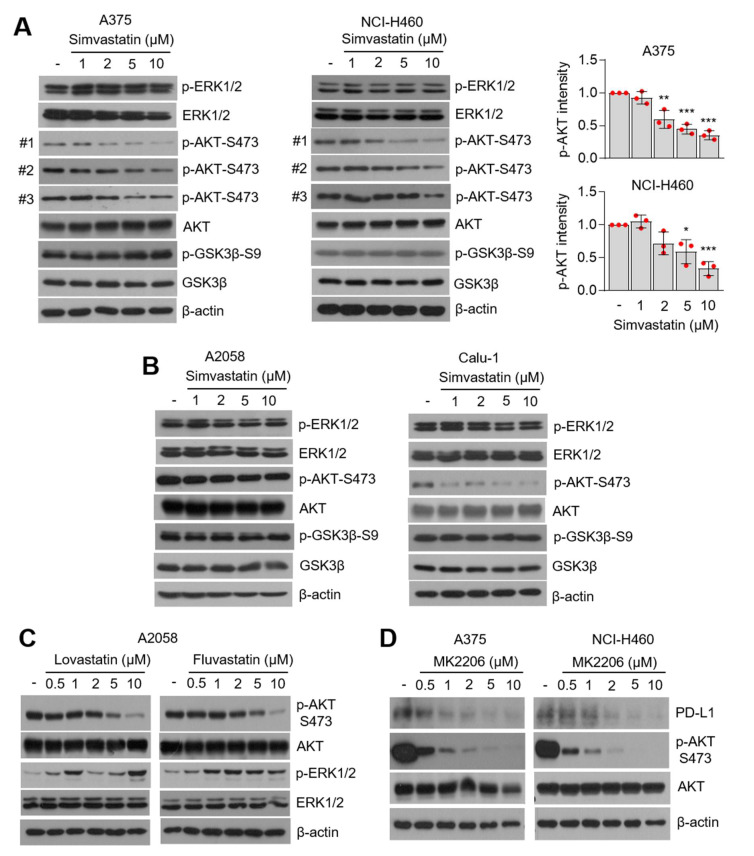
Figure 4.
Inhibition of AKT-signaling involved PD-L1 suppression by statins. (A) Simvastatin decreased phosphorylation of AKT but not ERK1/2 and GSK3β. A375 and NCI-H460 cells were incubated with different concentrations of simvastatin for 12 h, as indicated. Phosphorylated AKT protein levels were measured by using western blotting. Phosphorylated AKT intensity was quantified and represented by Image J and Graphpad Prism. Each phosphorylated AKT protein level in the statins-treated sample was compared to the vehicle sample. The values represent the mean ± SD from the three independent experiments (#1, #2, and #3) performed. Values represent mean ± SD. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 and *** p < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA, followed by an appropriate post hoc test for the comparison between two experimental groups. (B) Simvastatin suppressed AKT phosphorylation in A2058 and Calu-1 cells. (C) Lovastatin and Fluvastatin attenuated AKT phosphorylation. (D) A selective AKT inhibitor, MK2206, decreased PD-L1 expression in lung cancer (NCI-H460) and melanoma (A375) cells. DMSO as a vehicle or different concentrations of MK2206 were treated in NCI-H460 and A375 cells, and were incubated for 6 h. Protein levels were measured by using western blotting.