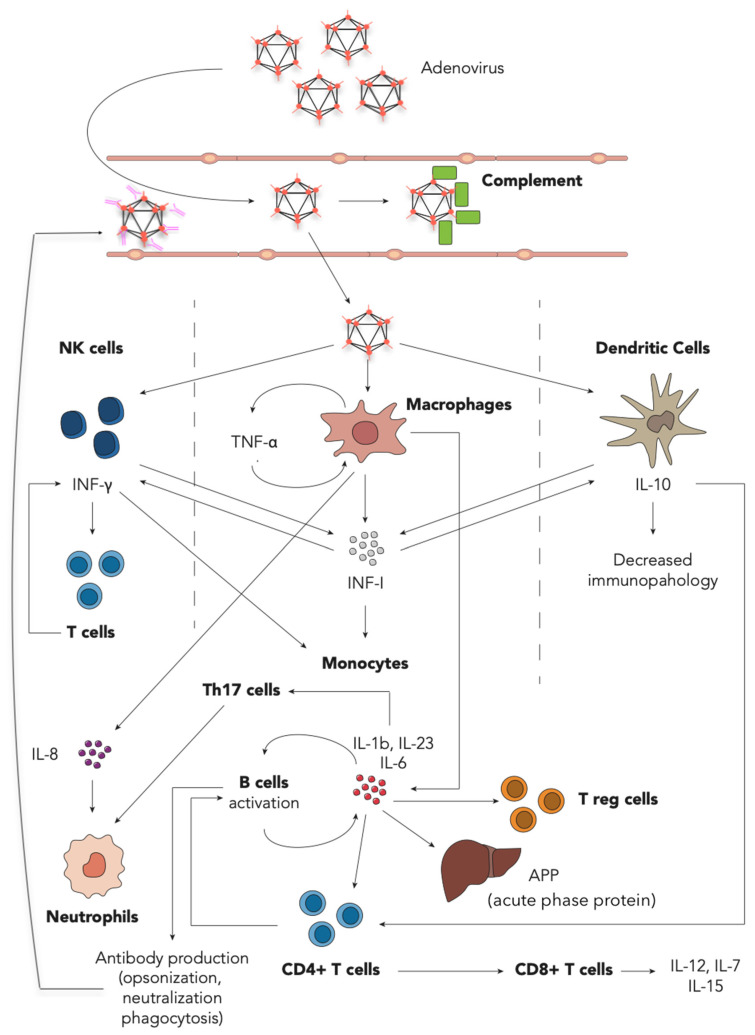
Figure 1.
Adenovirus–host interaction during the first days of acute infection. On the top is the reported innate immune response starting with HAdV entry, blood stream invasion, complement activation and C3a release to promote opsonization and phagocytosis. Below, at target organ or tissue, interaction between HAdV and effector of the innate immune response is shown. The entering and sensing of HAdV by Natural Killer (NK) cells, macrophages and Dendritic Cells (DC) (through either penetration [34], phagocytosis of opsonized HAdV or CD46, Sialic Acid, integrins and MHC I interaction [90]) stimulates the production of Type I interferons (IFN-I). IFN-I is secreted in large amounts mainly by specialized DC, and, together with IL-12, IL-15, IL-18 (not shown) and drives the secretion of IFN-γ in NK cells. IFN-I enhances macrophage phagocytosis, activation and the expression of MHC I and MHC II [91]. The former enhances recognition of infected cells by cytotoxic T cells, and the latter, in antigen presenting cells, promotes the presentation and activation of the CD4+ T cell-response. Type I IFN and IFN-γ drive an overall antiviral response, promoting intracellular viral clearance and guiding the T cell response [91]. Moreover, NK cell-derived IFN-γ promotes further maturation and activation of DC and macrophages. IL-8 produced the course of the disease early and exerts its actions mainly on neutrophils, resulting in migration to the site of infection. TNF-α, an acute phase cytokine produced in large amounts by DCs, exerts proinflammatory actions on cells (cytokine production, expression of adhesion molecules, chemotaxis) and tissues (edema, cellular growth) partially counterbalanced by the IL-10 effect on immune-mediated tissue damage or immunopathology. At the bottom, both elements of the adaptive and innate immune response are shown. Proinflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-23 and IL-1β) are secreted by activated macrophages and DC and induce acute phase protein (APP) production in the liver and the adaptive cellular and humoral response [33]. Antigen presentation to CD4+ T cells (together with membrane co-stimulants and the presence IL-10) guides proliferation and differentiation of B cells, T helper 17 (Th17) cells and cytotoxic T cells (CD8+ T cells). Among other functions, B cells are committed to antibody production, CD8+ T cells induce apoptosis of infected cells and proinflammatory cytokine secretion (IL-12, IL-7, IL-15) [92], and Th17 could aggravate the inflammatory response by recruiting inflammatory cells and cytokine production. Conversely, Treg (induced during T cell response) plays a major role in counteracting immune-mediated tissue damage.