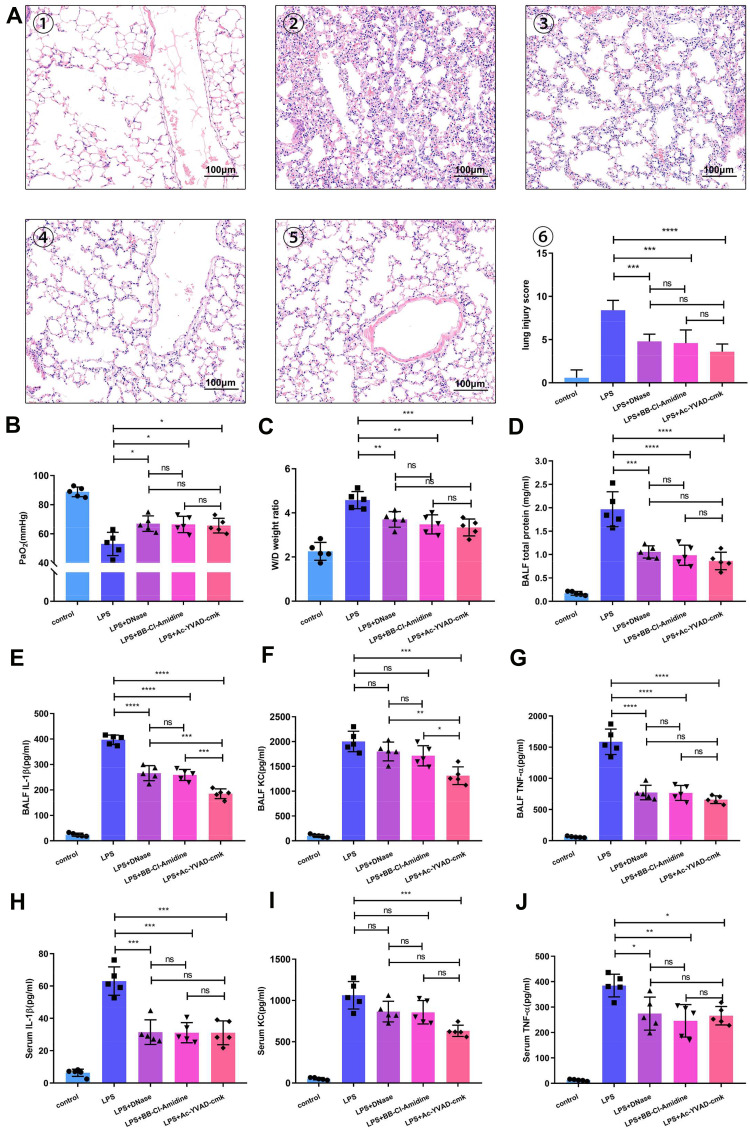
Figure 4.
NET-targeting agents and inhibition of alveolar macrophage pyroptosis provide similar protection against ARDS. (A) Administration of Ac-YVAD, DNase I or BB-Cl-amidine significantly reduced lung damage in LPS-challenged mice. Representative H&E-stained sections showing a significant improvement in the lungs of Ac-YVAD-, DNase I- or BB-Cl-amidine-treated mice. ① Sham-treated mice, ② LPS-treated mice, ③ DNase I plus LPS-treated mice, ④ BB-Cl-amidine plus LPS-treated mice, and ⑤ Ac-YVAD plus LPS-treated mice (200X). Administration of Ac-YVAD, DNase I or BB-Cl-amidine improved (B) the PaO2 of LPS-challenged mice and reduced (C) the weight/dry ratio of lung tissue and (D) the protein level in the BALF of LPS-challenged mice. BALF and serum (E and H) IL-1β, (F and I) KC, and (G and J) TNF-ɑ levels were all notably decreased in the DNase I, BB-Cl-amidine or Ac-YVAD plus LPS groups compared with the LPS-challenged group (n=5 mice). (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001).
Abbreviations: ARDS, acute respiratory distress syndrome; BALF, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; KC, keratinocyte-derived cytokine; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α.