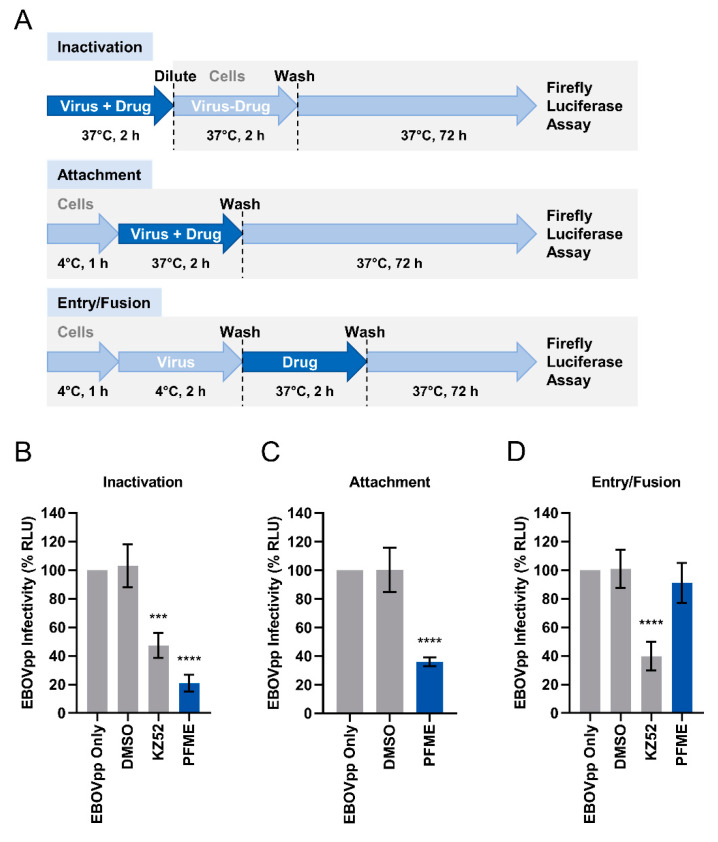
Figure 5.
PFME Effectively Inactivates EBOVpp and Blocks Viral Attachment to Host Cells. (A) Schematics of the synchronized infection assay on early viral entry. (B) Effect of PFME (30 μg/mL) treatment on cell-free EBOVpp (final MOI = 0.01). (C) Effect of PFME (30 μg/mL) treatment on EBOVpp (MOI 0.01) viral attachment. (D) Effect of PFME (30 μg/mL) treatment on EBOVpp (MOI 0.01) viral entry/fusion. Anti-GP antibody KZ52 (25 μg/mL), which specifically prevents the formation of fusion-activated EBOV GP [32], was included as a positive control for inactivation and entry/fusion assays. Luciferase reporter assay was performed at 72 h to evaluate EBOVpp infectivity (%). DMSO (0.01%) treatment served as negative control. Data are expressed as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. Asterisks (*) denote statistical significance: *** p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001.