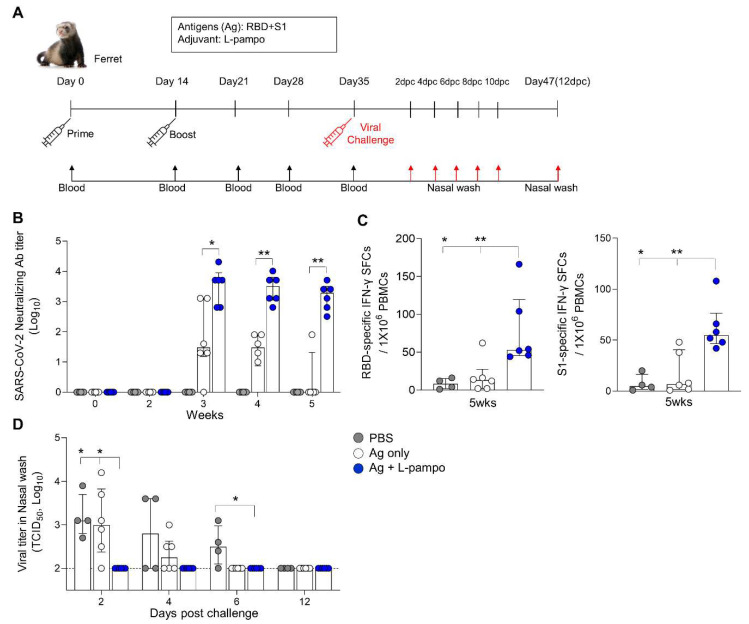
Figure 5.
RBD and S1 antigens with L-pampo induce robust humoral and cellular responses in the ferret model. (A) A schematic of the immunization and virus challenge strategy in the ferret model. Ferrets (total n = 16, n = 4/PBS; n = 6/Ag only; n = 6/Ag + L-pampo) were immunized with the SARS-CoV-2 antigens (RBD and S1 with 30 μg per each) with L-pampo i.m. on day 0 and day 14. The antigen-only and PBS groups were as controls. On day 35, ferrets were intranasally challenged with 105.5 50% tissue culture infective doses (TCID50/mL) SARS-CoV-2 (Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; resource no. 43326) under anesthesia. Blood was collected every week for 5 weeks from the first immunization. After virus challenge, the nasal wash was collected on days 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and 12. (B) Neutralizing antibody production on day 35 prior to challenge of virus. (C) On day 35, ferret PBMCs were stimulated with the RBD or S1 antigen and RBD or S1-specific IFN-γ-secreting cells were analyzed as SFCs by ELISPOT assay. (D) Viral load in nasal wash on days 2, 4, 6, and 12 after virus challenge by using a TCID50 assay. Dotted lines represent lower limits of detection. Data shown are median ± IQR. Each dot represents an individual ferret. Data reflect 2 independent experiments (n = 2/PBS group; n = 3/Ag only or Ag + L-pampo group in single experiment). * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; two tailed Mann–Whiteny test (B); one way ANOVA with the Tukey’s test (C,D).