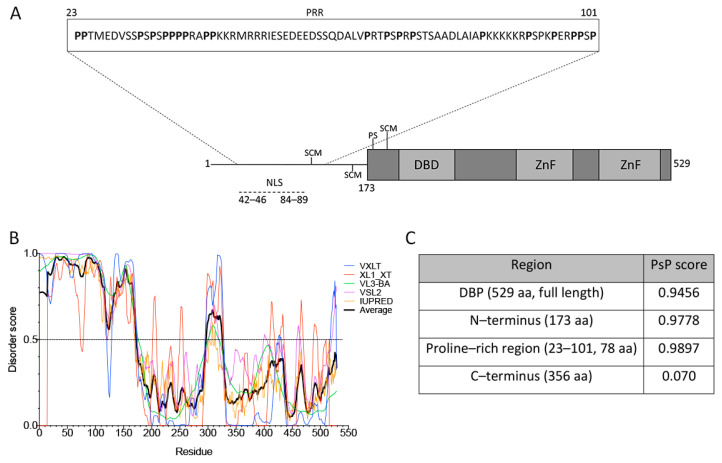
Figure 2.
DBP has sequence features of proteins that drive phase transitions. (A) Schematic representation of the HAdV-5 DBP. The N-terminal line represents the predicted intrinsically disordered region (IDR) from aa residues 1–173. The protein crystal has been resolved for aa residues 174–529 (gray boxes), showing that the central region forms a globular core which is composed of α-helices and ß-sheets, and a flexible hinge at the C-terminus. The DNA binding domain (DBD), zinc-fingers (ZnF), the known SUMO conjugation motifs (SCM) and phosphorylation sites (PS) as well as the nuclear localization signal (NLS) are indicated. The inset shows the proline-rich region (PRR) from aa residues 23–101, as predicted by Motif Scan. (B) The VXLT, XL1_XT, VL3-BA, VSL2, and IUPRED predictors were used for protein disorder analysis. An IDR was consistently predicted at the N–terminus (disorder score above 0.5). The black line represents the average score of all six algorithms for each amino acid residue. (C) PSPredictor (PSP) scores for different domains and motifs of DBP. PSPredictor scores from 0–1, a value above 0.5 indicates the peptide/protein is predicted to induce phase separation.