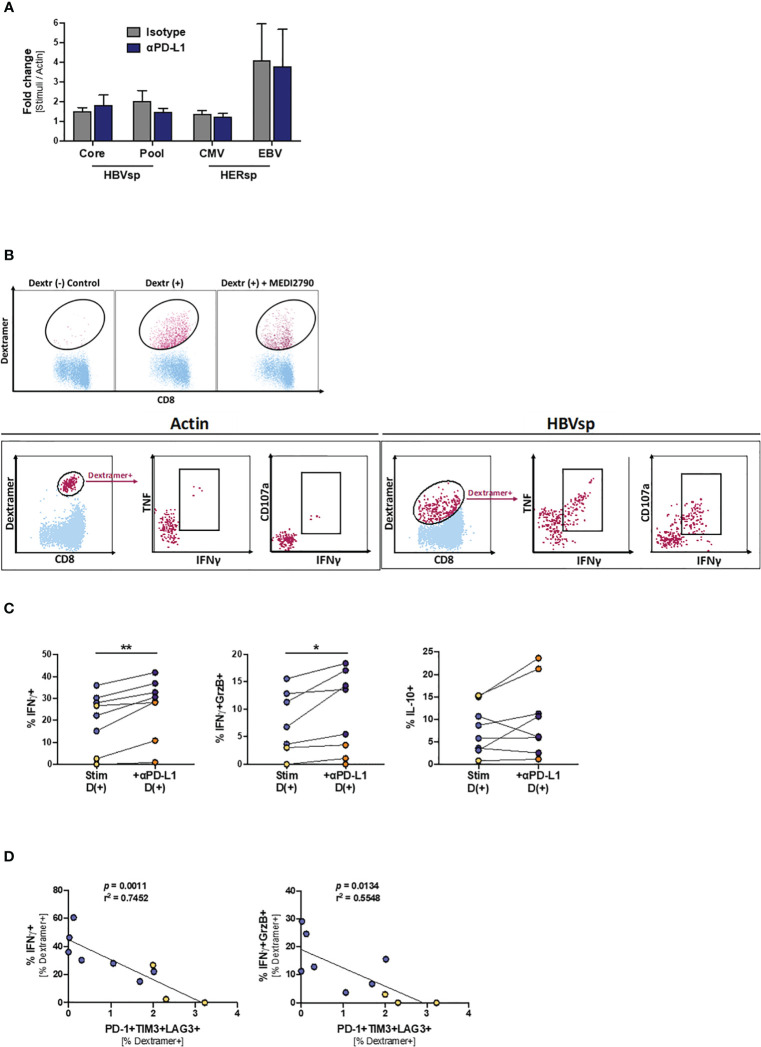
Figure 6.
PD-L1 blockade increases the frequency of IFNγ-producing Ag-specific CD8 T cells. (A) Effect of PD-L1 blockade on the proliferation levels of Ag-specific CD8 T cells. (B) Representative flow plots showing the gating strategy for intracellular cytokine staining of dasatinib-treated HBV-specific CD8 T cells. Dextramer-positive CD8 T cells (maroon) are overlaid on bulk CD8 T cells (light blue). While cytokines cannot be detected on samples stimulated with Actin negative control (left panel), dasatinib-treated stimulated HBV-specific T cells accumulate both cytokines and degranulation markers (right panel). (C) Effect of PD-L1 blockade in IFNγ (left panel), IFNγ+GrzB+ (middle panel) and IL-10 (right panel) production. Blue dots show HERPES-specific stimulations (CMV or EBV) while orange dots show HBV-specific stimulations (pool). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.001; Wilcoxon signed rank test. (D) Linear regression showing the negative correlation between Ag-specific IFNγ production and the frequency of highly exhausted (LAG3+TIM3+PD-1+) Ag-specific CD8 T cells. Blue dots show HERPES-specific stimulations (CMV or EBV) while orange dots show HBV-specific stimulations (pool).