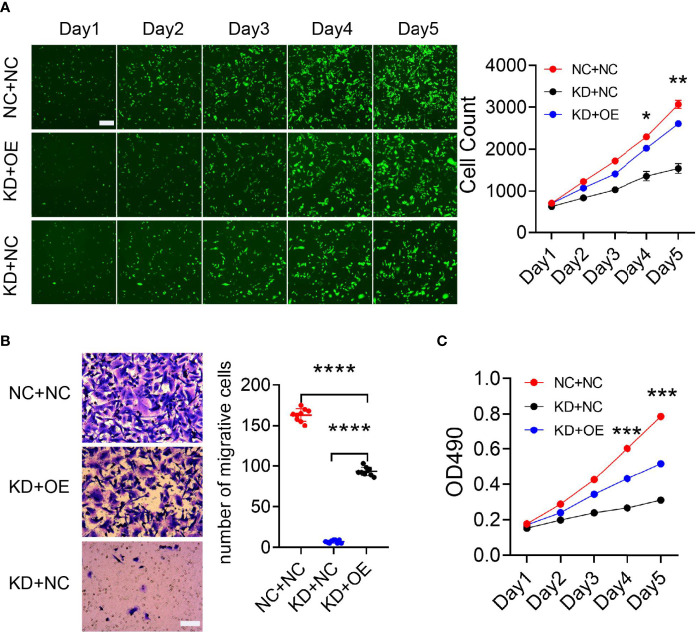
Figure 7.
The MDA-MB-231 cell line was used to verify the functional restoration of HLA-B interaction protein genes. (A) The proliferation ability of the cells was evaluated with Celigo apparatus for 5 consecutive days. (B, C) Transwell plate and MTT reagent were used to detect cell migration and cell viability, respectively. These experiments showed that HLA-B protein could restore the proliferation and migration abilities of breast cancer cells, thus further verifying the existence of an interaction between B4GALNT2 and HLA-B protein molecules. (A) Scale bar=100 μm; (B) Scale bar=50 μm. Note: NC+NC=normal control group; KD+OE=knockdown of the B4GALNT2 gene + the overexpressed HLA-B gene; KD+NC=knockdown of the B4GALNT2 gene, only. Note: for the 4 positive interaction proteins identified (CLU, AXL, HLA-B and EIF4A2), an interference or expression vector was constructed, thus achieving overexpression of the positive interaction protein while inducing interference with the target gene in a cell line. The Celigo instrument scanned the changes in cell proliferation ability for 5 consecutive days, and verified the functional restoration of the downstream mechanism genes on the target gene. Only the HLA-B gene had an obvious functional restoration effect. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.