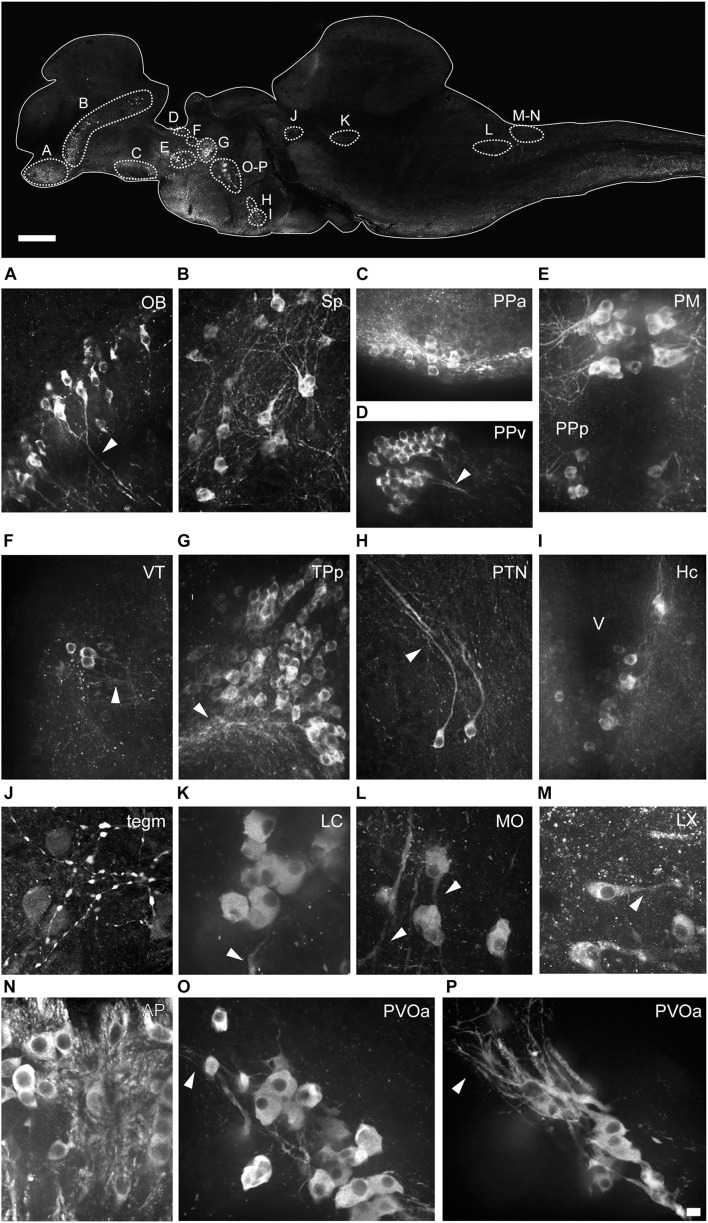
FIGURE 4.
Morphology of the different types of TH+ neurons in the brain of Nothobranchius furzeri. The upper image illustrates the positions of TH+ cells in a para-sagittal section of the brain. (A–P) High resolution images of TH+ neurons present in the olfactory bulb (OB; A), subpallium (Sp; B), anterior preoptic nucleus (PPa; C), ventral periventricular pretectal nucleus (PPv; D), magnocellular preoptic nucleus (PM) and parvocellular portion of preoptic nucleus (PPp; E), ventral thalamus (VT; F), periventricular nucleus of posterior tuberculum (TPp; G), posterior tuberal nucleus (PTN; H), caudal hypothalamus (Hc; I), mesencephalic tegmentum (Tegm; J), locus coeruleus (LC; K), medulla oblongata (MO; L), vagal lobe (LX; M), area postrema (AP; N), and in the rostral (O) and caudal (P) clusters of the paraventricular organ-accompanying cells (PVOa). Arrowheads points to TH+ neuronal processes. For abbreviations see list. Scale bar, 500 μm (upper panel) and 10 μm (A–P).