Figure 4.
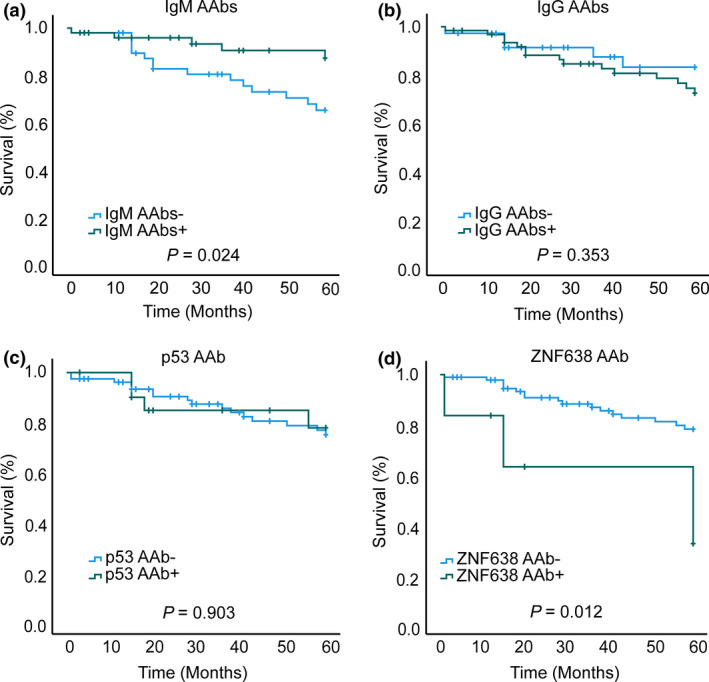
Autoantibodies and patient survival. Kaplan–Meier survival analysis of autoantibody panels revealed (a) cumulative presence of IgM autoantibodies (+ seropositive, − seronegative) was significantly associated with improved survival (IgM+ n = 50, IgM− n = 49) (log‐rank test, P = 0.024), (b) cumulative presence (+) and absence (−) of IgG autoantibodies had no association with overall patient survival (n = 63, IgG− n = 36) (log‐rank test, P = 0.353), (c) presence of anti‐p53 IgG autoantibodies showed no association with overall patient survival (p53+ n = 21, p53− n = 78) (log‐rank test, P = 0.903) and (d) presence of anti‐CTLC‐associated antigen se33‐1 (ZNF638) IgG autoantibodies was associated with poor 5‐year survival in CRC patients (ZNF638+ n = 6, ZNF638− n = 93) (log‐rank test, P = 0.012).
