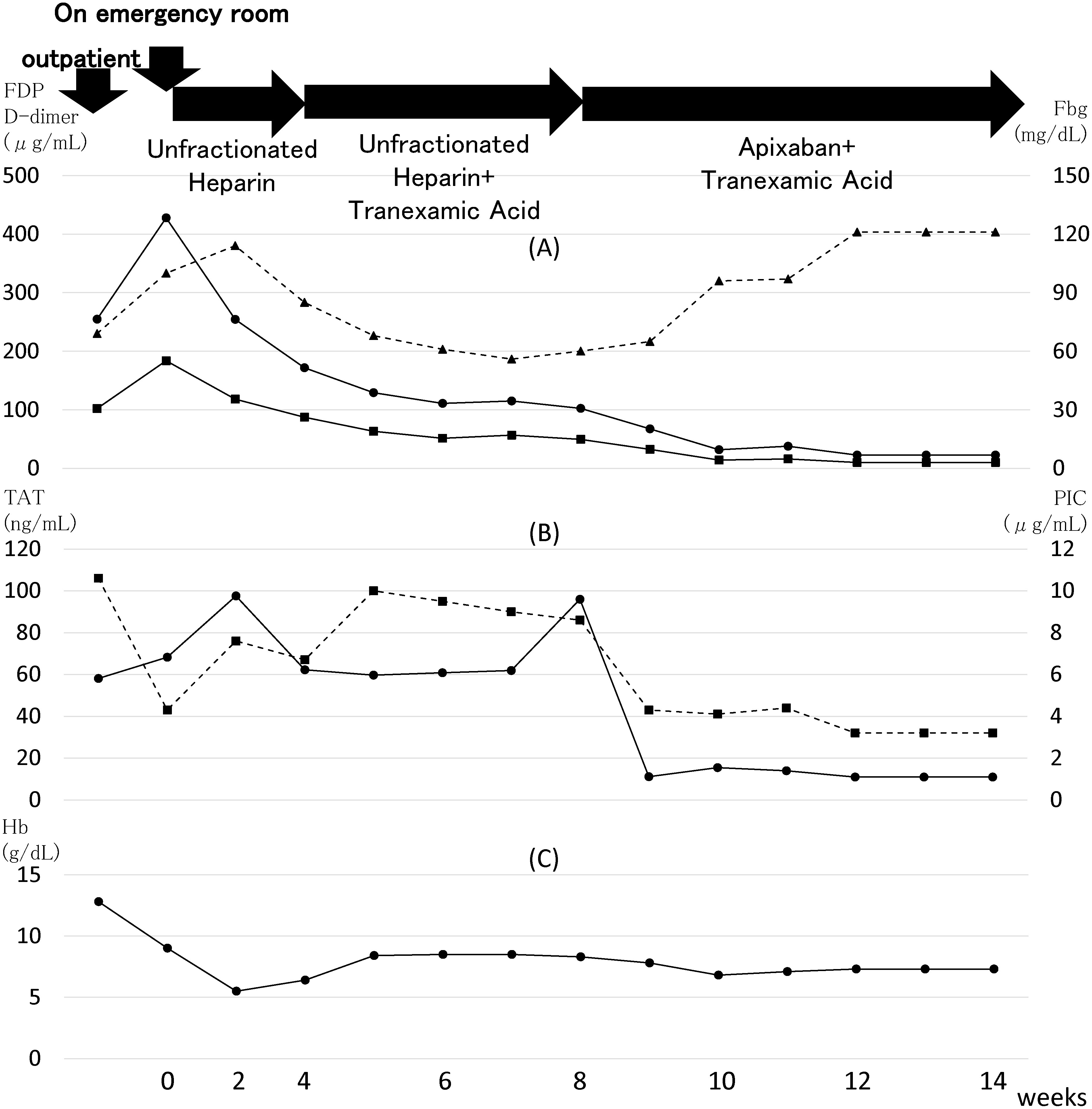
Fig. 2 Changes in results of coagulation testing and hemoglobin (Hb). Numbers at the bottom represent the length of hospital stay in weeks, with time on admission set as 0. (A) Changes in fibrin/fibrinogen degradation products (FDP), D-dimer, and fibrinogen (Fbg). ●: FDP; ■: D-dimer; ▲: Fbg. FDP and D-dimer temporarily decreased after starting treatment with unfractionated heparin alone, and both decreased further after switching to apixaban. Fbg temporarily increased because of the presence of infection at the time of admission to our hospital but decreased as infection improved. During the period of combination treatment with unfractionated heparin and tranexamic acid, Fbg was kept at approximately 60 mg/dL but clearly increased after starting combination treatment with apixaban and tranexamic acid. (B) Changes in thrombin–antithrombin complex (TAT), a marker for the activation of coagulation, and plasmin–α2 plasmin inhibitor (α2PI) complex (PIC), a marker for the activation of fibrinolysis. ●: TAT; ■: PIC. Neither TAT nor PIC decreased clearly until combination treatment with apixaban and tranexamic acid was started. (C) Changes in Hb. Despite the changes shown in (A) and (B), the improvement in anemia is poor and red blood cell transfusions (280 mL each) have been required once every two or three days.