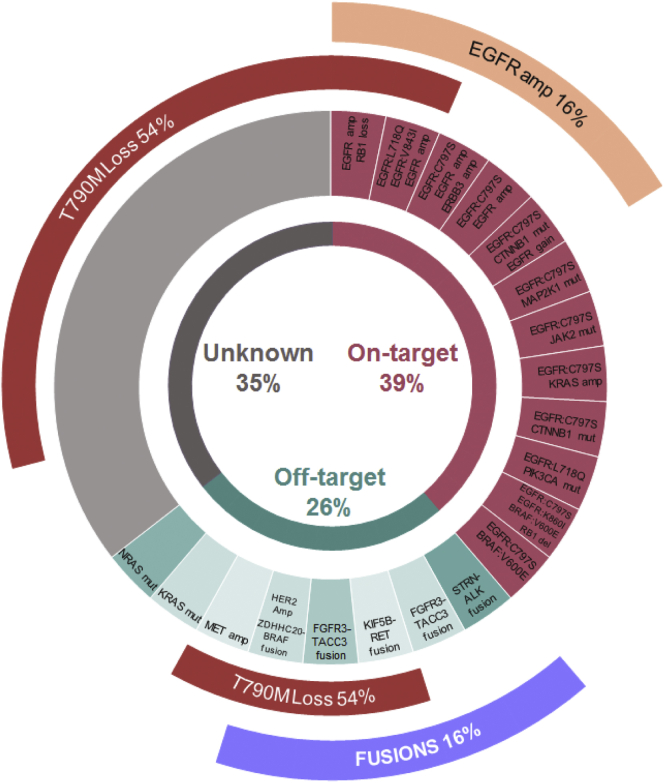
Figure 1.
Distribution of resistance alterations to third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (n = 31). A total of 28 patients tested positive for T790M pre-osimertinib (two received osimertinib as first-line and T790M was not investigated at baseline in one patient). Among them, 15 (54%) lost this mutation at osimertinib progression biopsy. T790M, Thr790Met mutation of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR); ERBB3, Erb-b2 receptor tyrosine kinase; CTNNB1, catenin beta 1; MAP2K1, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1; JAK2, Janus kinase 2; PIK3CA, phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha; RB1, retinoblastoma gene; STRN, striatin gene; ALK, anaplastic lymphoma kinase; FGFR3, fibroblast growth factor receptor 3; TACC3, transforming acidic coiled-coil containing protein 3; KIF5B, kinesin family member 5B; RET, ret proto-oncogene; HER2 Amp, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 amplification; ZDHHC2, zinc finger DHHC-type palmitoyltransferase 20; MET; met proto-oncogene (hepatocyte growth factor receptor); NRAS, N-ras proto-oncogene (neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog).