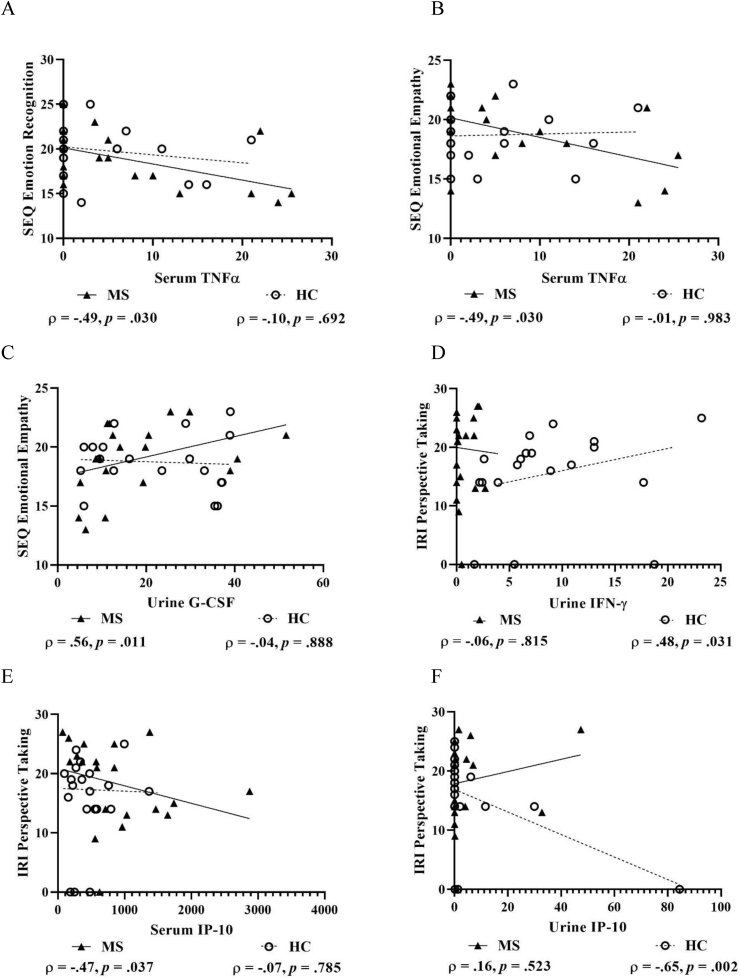
Fig. 4.
Scatterplots with selected correlations between pro-inflammatory markers and subjectively assessed social-cognitive measures in people with multiple sclerosis and matched healthy control participants. Figures show pro-inflammatory serum TNF-α and both SEQ Emotion Recognition (A) and SEQ Emotional Empathy (B), urine G-CSF and SEQ Emotional Empathy (C) urine IFNγ and IRI Perspective Taking (D), serum IP-10 and IRI Perspective Taking (E), and urine IP-10 and IRI Perspective Taking (F). G-CSF, Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; IFN-γ, Interferon-gamma; IP-10, Interferon-gamma inducible protein 10; IRI, Interpersonal Reactivity Index; SEQ, Social and Emotional Questionnaire; and TNFα, Tumour necrosis factor-alpha. An alternative analysis was performed on Figure F (urine IP-10 & IRI Perspective Taking), removing the HC outlier, which showed minimal change in the strength, direction and significance of the correlation (ρ = −0.60, p = .007); thus, this case was retained. Concentrations are shown in fluorescence intensity values for serum and fluorescence intensity/creatinine values for urine.