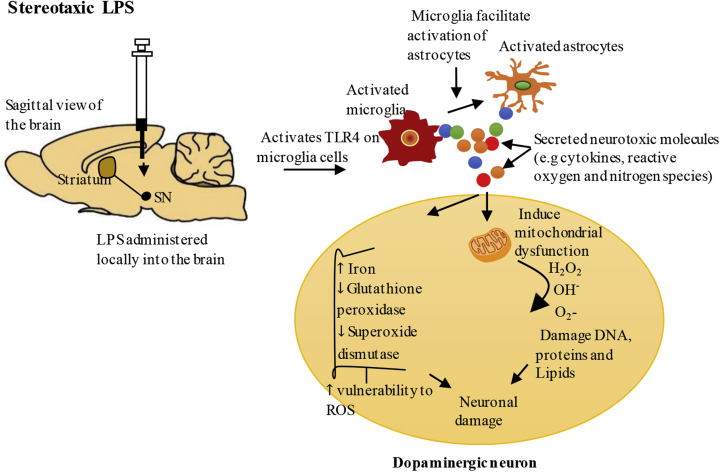
Fig. 1.
Stereotaxicadministration ofLPS – the proposed mechanisms leading todopaminergicneuron degeneration.
Stereotaxic administration of LPS (delivered directly into the local brain environment) can activate Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) on microglia cells resulting in the production of inflammatory cytokines (e.g.TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IFN-γ) and free radicals (e.g. NO and O2-) in the brain (Liu and Bing, 2011). Activated microglia facilitate the activation of astrocytes which augment the inflammatory response through additional production of inflammatory cytokines, and reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Excessive production of these neurotoxic molecules could impair mitochondrial function, resulting in impaired energy metabolism and additional production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and can reduce antioxidants such as glutathione peroxidase and superoxide dismutase in the brain (Hauser and Hastings, 2013; Park et al., 2018; Villacé et al., 2017). Stereotaxic LPS also increases iron levels in the substantia nigra (SN), which could catalyse the Fenton reaction of superoxide (O2-) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to yield hydroxyl radicals (OH−) which are toxic to the neurons (Hauser and Hastings, 2013).