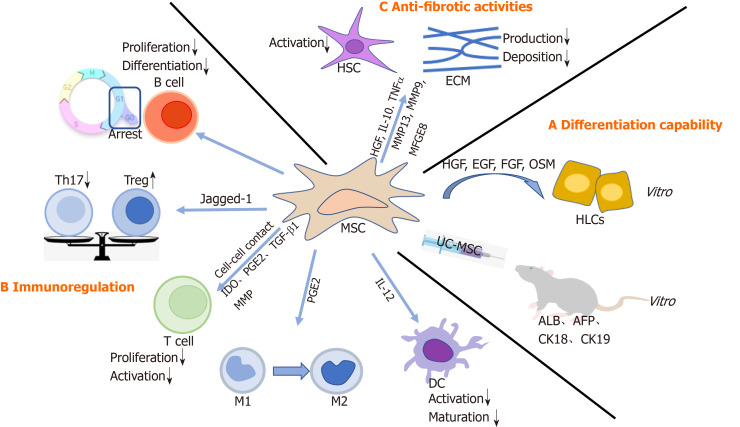
Figure 1.
The mechanism of mesenchymal stem cells in liver diseases. A: Mesenchymal stem cell (MSCs) differentiate into hepatocyte-like cells both in vitro and in vivo; B: MSCs modulate effector cells of innate and adaptive immune systems; C: MSCs alleviate liver fibrosis. MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell; UC-MSC: Human umbilical cord-derived MSC; HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor; EGF: Epidermal growth factor; FGF: Fibroblast growth factor; OSM: Oncostatin M; HLCs: Hepatocyte-like cells; ALB: Albumin; AFP: Alpha-fetoprotein; CK18: Cytokeratin 18; CK19: Cytokeratin 19; DC: Dendritic cell; M1: M1 macrophage; M2: M1 macrophage; IL-12: Interleukin 12; PGE2: Prostaglandin E2; IDO: Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinases; TGF-β1: Transforming growth factor-β1; Th17: T helper cells 17; Treg: Regulatory T cells; HSC: Hepatic stellate cell; IL-10: Interleukin 10; TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor α; MFGE8: Milk factor globule EGF 8; ECM: Extracellular matrix.